Figure 6.
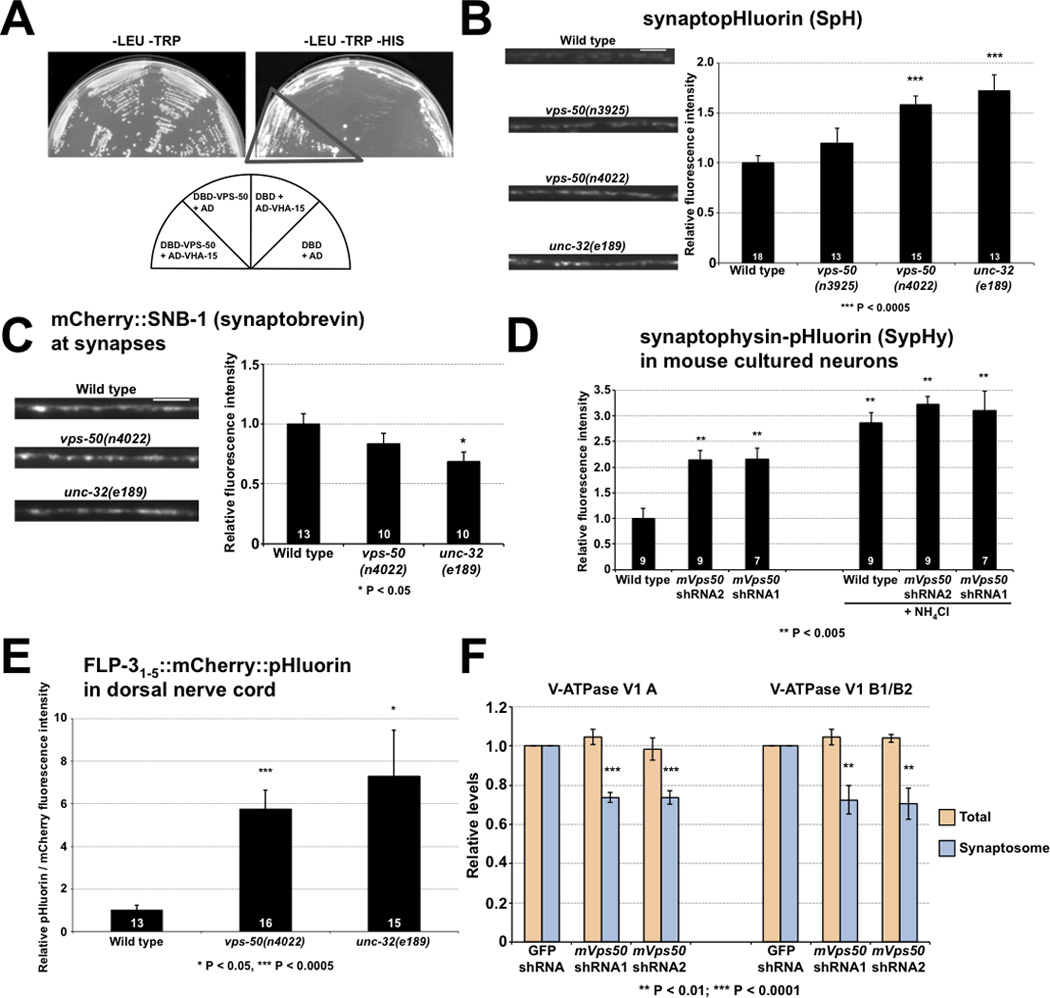
Disruption of vps-50 in C. elegans or of its murine homolog mVps50 in mouse cultured neurons similarly impair synaptic vesicle acidification. A) VPS-50 can associate with the V-ATPase subunit VHA-15 in the yeast two-hybrid assay. Growth occurred on media lacking histidine (dark triangle). B) vps-50 mutants have a synaptic vesicle acidification defect. Representative micrographs and quantification of synaptopHluorin (SpH) fluorescence levels. SpH fluorescence is quenched by acidic pH; thus, increased fluorescence levels correspond to increased pH. Mutants defective in the V-ATPase complex subunit gene unc-32 were used as an acidification-defective control [25]. C) vps-50 mutants did not have elevated levels of synaptobrevin SNB-1 at synapses, indicating that the higher SpH (a SNB-1::pHluorin fusion) fluorescence levels observed in vps-50 and unc-32 mutants were not caused by elevated levels of SpH at synapses. Representative fluorescence micrographs and quantification of mCherry::SNB-1 levels at synapses. D) Knockdown of mVps50 in mouse primary cultured cortical neurons led to a synaptic vesicle acidification defect. Quantification of SypHy (synaptophysin-pHluorin fusion) fluorescence levels with or without knockdown of mVps50. Higher fluorescence levels correspond to higher pH. SypHy expression levels in wild-type and mVps50 knocked-down neurons are similar, as addition of NH4Cl to increase the intravesicular pH to 7.4 led to similar SypHy fluorescence levels in both. E) vps-50 mutants have a dense-core vesicle acidification defect. pHluorin and mCherry fluorescence intensities were quantified from FLP-31–5::mCherry::pHluorin reporter. An increased pHluorin/mCherry fluorescence ratio indicates increased pH. Mutants defective in the V-ATPase complex subunit gene unc-32 were used as an acidification-defective control. F) Knockdown of mVps50 in mouse primary cultured cortical neurons reduces the amount of V-ATPase (V1) subunits A and B in the synaptosomal fraction. Levels of V-ATPase soluble subunits A and B were quantified in total protein extracts and in synaptosomal fractions in wild-type and mVps50 knockdown primary cultured neurons. n = 6. Scale bars: 5 µm. Bar graphs, n values (number of animals or neurons) are indicated on bars, means ± SEMs. See also Figure S5.
