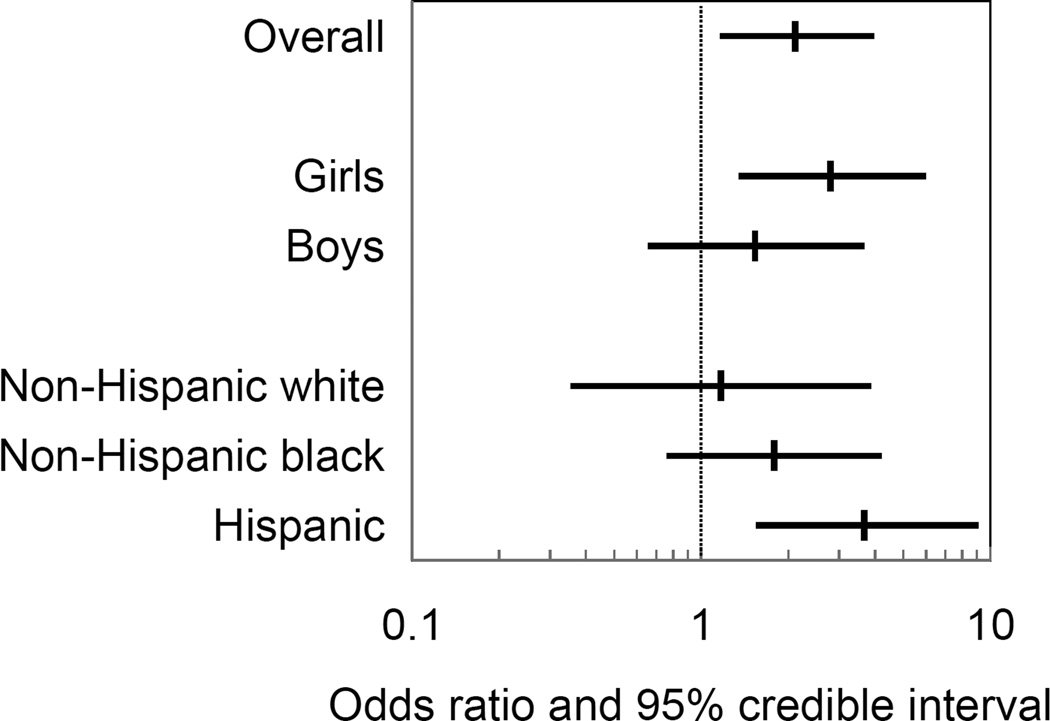
Figure 1.
Posterior mean of odds ratios and 95% credible intervals for the association of a one standard deviation increase in natural log urinary MCPP concentrations with overweight/obese status among children aged 4 to 7 years (N=707; 1,416 follow-up visits), overall and by child’s sex and race/ethnicity. Associations estimated in multiple metabolite logistic mixed effects regression models adjusted for cohort, maternal race/ethnicity, maternal age at delivery, maternal education, maternal work status during pregnancy, maternal pre-pregnancy BMI, maternal height, gestational weight gain, maternal smoking during pregnancy, natural log creatinine, calendar date of urine collection, parity, child’s sex, breastfeeding, and months of age at follow-up.