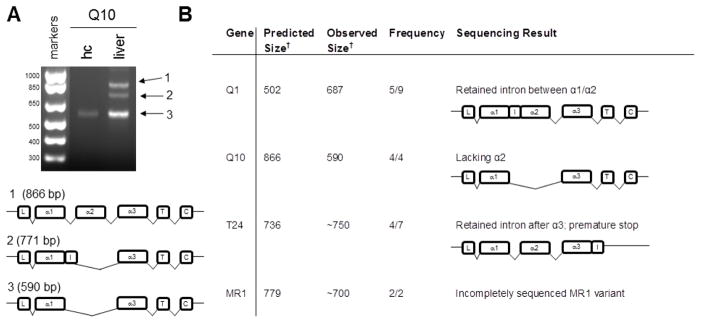
Figure 9. Alternative splicing of MHCI genes in whole hippocampus.
A. Products of smaller-than-expected size were detected using primers against the nonclassical MHCI Q10. The MHCI heavy chain is organized into eight exons, each of which encodes a functional domain. Exon 1 encodes the signal peptide, and exons 2, 3, and 4 encode the α1, α2, and α3 domains, respectively. The transmembrane domain is encoded in exon 5, and the short cytoplasmic tail is encoded by exons 6, 7, and 8. Sequencing confirmed that the products of unexpected size were splice variants of Q10 that both lacked the α2 domain, while one, which was detected in liver, included a retained intron (I). The α2-deficient transcript (3) was the only form of Q10 detected in hippocampus (hc). L, leader sequence; T, transmembrane domain; C, cytoplasmic domain, I, retained intron.
B. RT-PCR products larger or smaller than the predicted size were observed with twelve primer pairs. Frequency reported as number of times a band of that size observed in experiments using the same sample type where any band was detected with that primer set. Sequencing of several products confirmed their identity as an MHCI splice variant. Sequencing was inconclusive for experiments indicated with a “-“. †Size in base pairs.