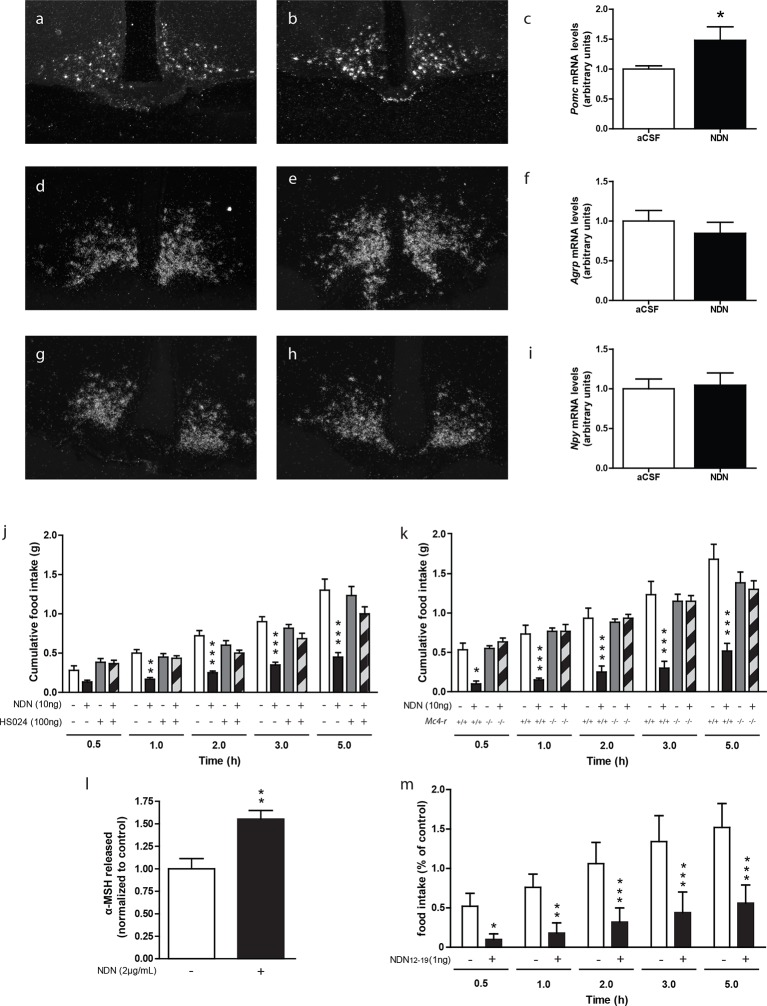
Figure 4. The melanocortin system relayes the anorexigenic effects of NDN.
(a–i) In situ hybridization analysis of Pomc mRNA levels in the mediobasal hypothalamic sections. Hypothalamic Pomc (a,b,c), AgRP (d,e,f) and Npy (g,h,i) mRNA levels from 18 hr-food deprived mice icv-injected with aCSF (a,d,g) or NDN (b,e,h; 100 ng) 2 hr before sacrifice. (c,f,i) Relative quantification performed in the ARC. Data were compared to aCSF injected mice as control (n=6, 7). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Unpaired Student’s t test: *p<0.05. (j) Mice fasted for 18 hr received icv injection of an MC4R-specific antagonist (HS024; 100 ng) alone or with NDN (10 ng) diluted in aCSF (n=5, 6). (k) Mc4r knock-out or wild type mice fasted for 18 hr were icv injected with NDN (10 ng). Mice had access to food 20 min after icv injection and cumulative food intake was measured at the indicated period (n=6). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Two-way ANOVA followed by a post-hoc multiple comparison Bonferroni test: *p< 0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. (l) Hypothalamic explants were preincubated in aCSF alone followed by an incubation with or without NDN (2 µg/ml). α-MSH released during incubation was normalized to the amount released during the preincubation period (n=5). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Unpaired t test: *p<0.05; NS, not statistically different. (m) Mice fasted for 18 hr were bilaterally injected in the MBH with NDN (1 ng). Mice had access to food 20 min after injection and cumulative food intake was measured at the indicated period (n=5). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Two-way ANOVA followed by a post-hoc multiple comparison Bonferroni test: *p< 0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11742.023