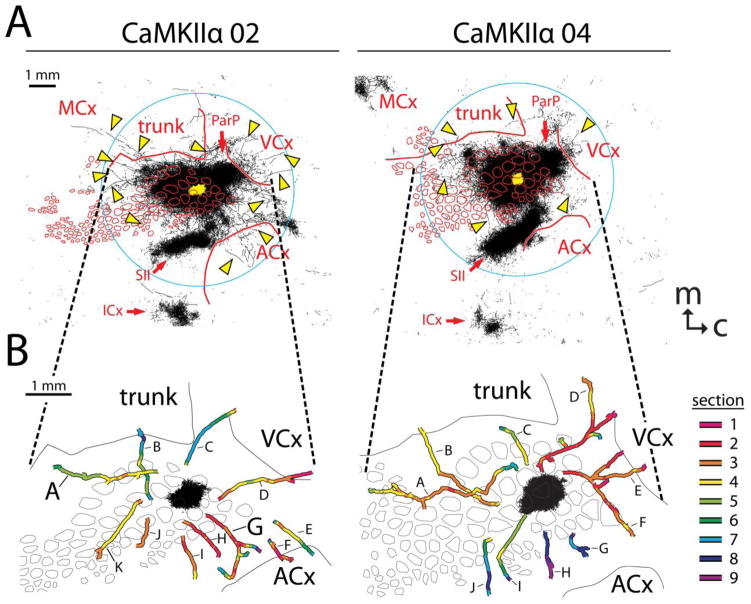
Fig. 11.
Projection patterns following supragranular injection of an AAV vector directing expression of YFP by way of a CaMKIIα promoter in order to restrict labeling to axons from excitatory cortical neurons. A. Tracings of axons detected in the nine most superficial 40-μm sections of flattened cortices were collapsed together as was shown in Fig. 2 for brains injected with the CMV promoter. As in the right panels of Fig. 2, thicker lines were used to better visualize the sparser axon segments (arrowheads) located outside of major specific projection targets. The yellow area in the center of each panel indicates the saturated immunostaining present in a section near layer 4 (the size of the injection). B. Locations of reconstructed long horizontal axons from the nine most superficial 40-μm transverse sections. Axon segments were stitched together and colored according to the section in which they were located, as described for Fig. 9. Letters refer to individual axons referenced in the text. Axons A and G from brain CaMKIIα 02 are further illustrated in Fig. 12. Axons labeled E and F in brain CaMKIIα 04 may represent a single continuous fiber; however, another axon crossed the proximal end of axon F in section 2 (red segment) at such a similar depth that the continuation of the fiber could not be unambiguously established. This figure represents only a sampling of the axons that could have been reconstructed in these brains. Dashed lines extending between A and B point out identical locations in the two illustrations. ACx, auditory cortex; VCx, visual cortex; MCx, motor cortex; ICx, insular cortex; ParP, posterior parietal cortex; SII, secondary somatosensory cortex; trunk, trunk region of primary somatosensory cortex; m, medial; c, caudal