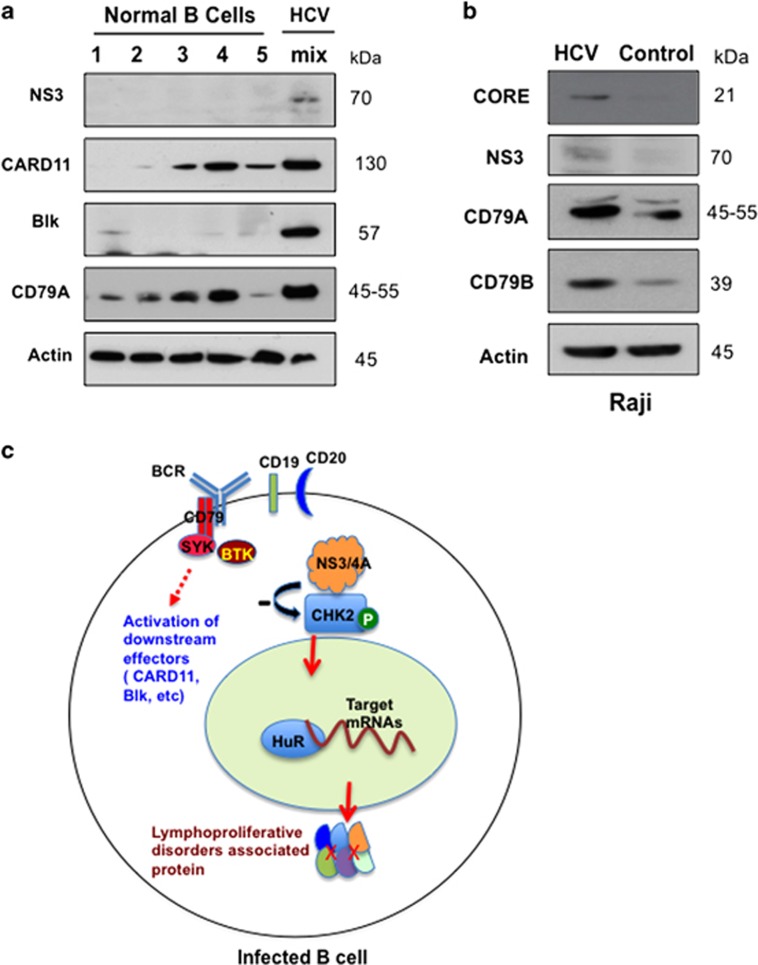
Figure 6.
HCV infection upregulates BCR signaling in human primary B cells and Raji cells. (a) Western blot analysis showing protein expression of NS3, CARD11, Blk and CD79A in lysates isolated from normal (five discrete patients) and HCV-infected (mix: pooled from eight patients) purified B cells. Actin was used as a loading control. (b) Protein expression of NS3, core, CD79A and CD79B in lysates isolated from control and HCV-infected Raji cells was detected by western blot analysis. (c) The model depicts a proposed mechanism for HCV-associated B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders. HCV NS3/4A interacts with CHK2 and downregulates CHK2 activity. Subsequently, this repressed CHK2 activity modulates HuR posttranscriptional regulation of a network of target mRNAs associated with B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders, preferentially those involved in the BCR signaling pathway.