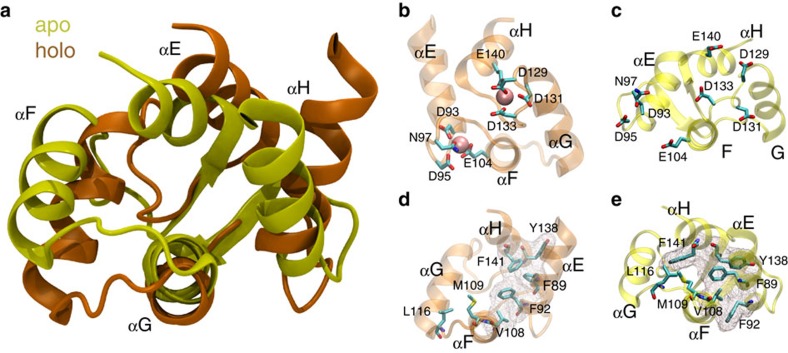
Figure 1. C-CaM conformational change upon Ca2+ binding.
(a) Comparison of the C-terminal domain from published structures of apo (1CFD) and holo (1CLL) CaM indicates the large-scale structural rearrangements that occur when Ca2+ binds. (b,c) In particular, repositioning of the Ca2+-ligating residues from solvent-exposed rotamers renders each EF hand competent to bind Ca2+. (d,e) Additionally, binding of Ca2+ induces repacking in the hydrophobic core and binding interface, enabling compact clustering of the aromatic residues outlined by the mesh.