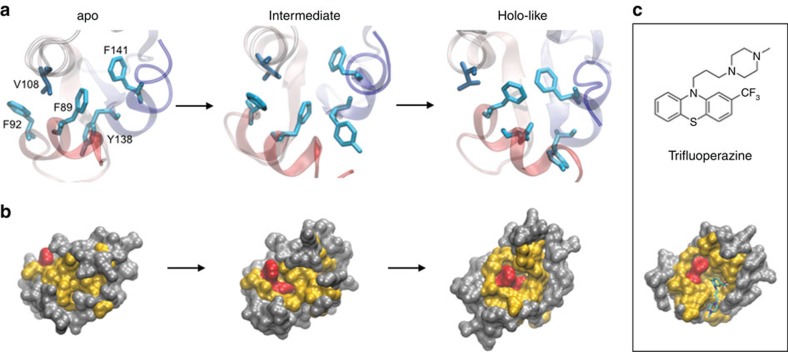
Figure 4. Hydrophobic repack determines the topology of the binding interface.
(a) Packing of Val108 between Phe92 and Phe89 is disrupted during the apo- to holo-like transition, which enables the formation of a compact aromatic cluster in the C-CaM core. (b) Surface representations of the apo, intermediate, and holo-like states show that repack exposes distinct surface topologies. Phe, all other hydrophobic, and polar residues coloured red, yellow and grey, respectively. (c) The Phe-lined cavity formed in the holo-like state is commonly accessed by bulky aromatic rings of binding partners, as shown in the crystal structure of holo CaM in complex with trifluoperazine. Only the C-terminal domain of this structure (1CTR) is shown.