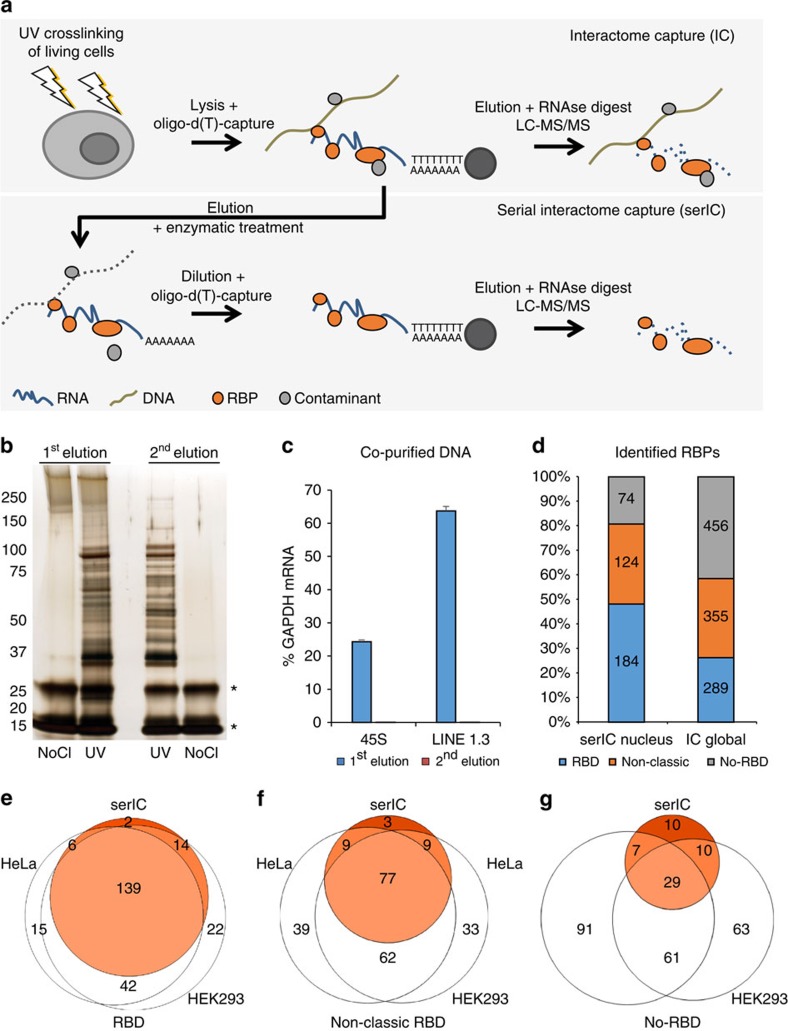
Figure 1. serIC recovers highly purified nuclear RBPs.
(a) Comparison of the IC and serIC methods. Irradiation of living cells with ultraviolet (UV) light at 254 nm induces covalent crosslinks between proteins and nucleic acids. After cell lysis, RBP–poly(A)-RNA complexes are captured by hybridization to oligo(dT) magnetic beads and washed under denaturing conditions. In IC, purified material is eluted and proteins are identified by LC–MS/MS (top). In serIC, eluted material is enzymatically treated to remove contaminating DNA. Free RBP–poly(A)-RNA complexes are diluted in the presence of high salt and detergent to disrupt residual non-crosslinked interactions, recaptured by hybridization to oligo(dT) beads and analysed by LC–MS/MS. (b) SDS–PAGE of proteins crosslinked to poly(A)-RNA. Nuclei from irradiated K562 cells were isolated and subjected to the serIC procedure. Protein–RNA complexes obtained after the first or second round of purification (first elution and second elution) were digested with RNAseA/T1, separated on a polyacrylamide-gradient gel, and visualized by silver staining. No UV-crosslinking was performed in controls (No Cl). Asterisks indicate RNase A/T1. (c) Elimination of DNAse contamination. qPCR measurement of eluate from the first and second round of purification was performed without reverse transcription to detect residual DNA. Levels of 45S rDNA and LINE 1.3 retrotransposon DNA in the first and second eluate are shown relative to GAPDH mRNA in the second eluate. Error bars show s.d. from two independent experiments. (d) Domain composition of the nuclear RNA interactome. Proteins identified by LC–MS/MS in serIC preparations from K562 nuclei, and in previous IC from HeLa15 and HEK293 (ref. 14) were grouped by the presence or absence of classical or non-classical RBDs as indicated. (e–g) serIC recovery of proteins with the GO association ‘nucleus' that were previously identified by IC in HeLa15 or HEK293 (ref. 14). Proteins containing classical (e), non-classical (f), or no RBDs (g) were compared separately.