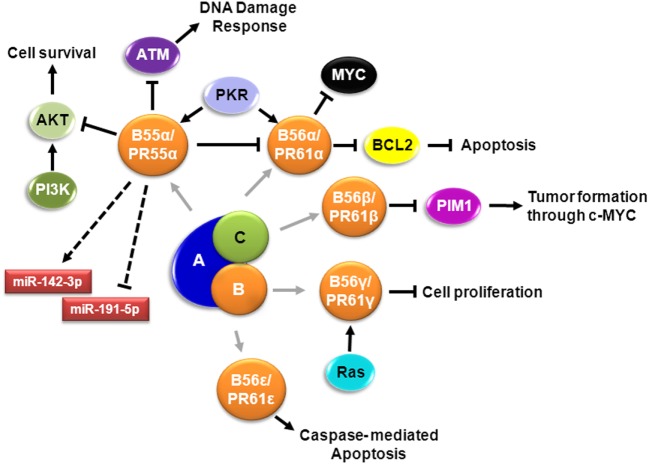
Figure 1.
Signaling pathways involving PP2A in AML. Schematic representation of known PP2A complexes involving different B regulatory subunits in AML cells. Cell survival is regulated by PR55α/B55α – mediated dephosphorylation of AKT (15, 16). PR55α/B55α also supports expression of miR-142-3p and suppresses expression of miR-191-5p, relevant miRNAs in AML (17). DNA damage response is impaired by dephosphorylation of ATM by PP2A-PR55α/B55α, which translocate to the nucleus by PKR (18). Extracellular survival signals activate SRC that suppresses the B subunit; when SRC is suppressed, PR55α/B55α is expressed, resulting in dephosphorylation of PKCα and suppression of PR61α/B56α protein expression, with concomitant induction of MYC (19). Apoptosis is regulated by activation of PR61α/B56α by PKR leading to dephosphorylation of BCL2 (20). PR61β/B56β regulates PIM1 contributing to tumor formation (21). PP2A-B56γ function in G2 is crucial to sustain normal G0/G1 control and this G2 PP2A function involves modulation of endogenous RAS signaling (22). PR61ϵ/B56ϵ, which is downregulated in AML, controls caspase-mediated apoptosis (23).