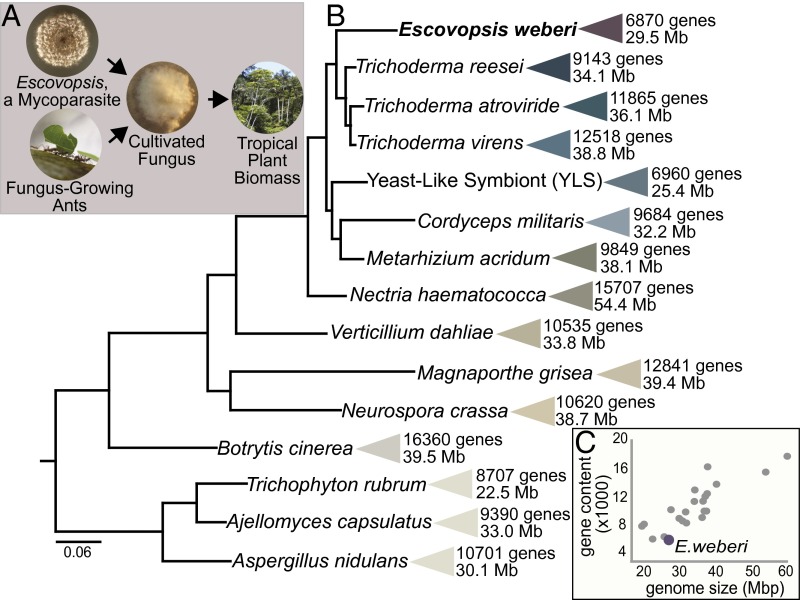
Fig. 1.
Escovopsis weberi, a specialized mycoparasite of the fungus-growing ant symbiosis, has a small genome compared with other Pezizomycotina fungi. (A) Both fungus-growing ants and the mycoparasite E. weberi use the ants’ cultivated fungi as their primary food source. The ability of the cultivated fungi to efficiently break down plant material gives both consumers access to the biomass of neotropical plants. (B) Size and protein-coding gene content of genomes of diverse fungi in the Pezizomycotina. Bayesian phylogeny estimated using partial amino acid alignments of three genes (Rpb1, Rpb2, ef1-α). All posterior probabilities are greater than 0.95. Phylogeny is rooted with Sacchormyces cervesiae (not shown). (C) Relationship between genome size and gene content. A list of genomes included in this panel is in SI Appendix, Table S1.