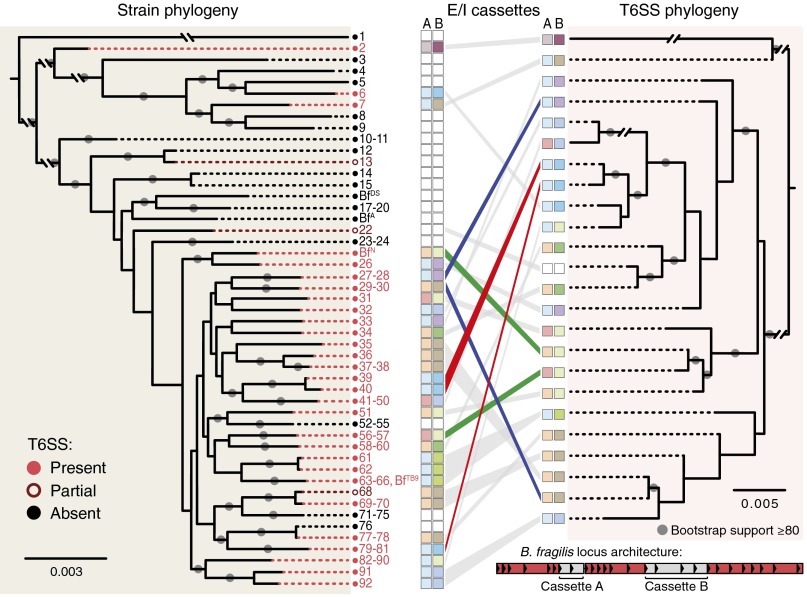
Fig. 2.
Comparative genomic analysis of B. fragilis strains reveals multiple independent acquisitions of T6SS loci and numerous putative effector/immunity cassettes. Whole-genome phylogeny (Left) of all 92 sequenced B. fragilis strains (Dataset S1, Table S1) is linked to T6SS locus phylogeny (Right) by gray and colored lines. T6SS locus architecture is conserved across T6SS+ B. fragilis strains, revealing three conserved, syntenic regions (red shading) and two variable, nonsyntenic regions (gray shading) within each T6SS locus (Inset). Putative effector/immunity repertoires of nonsyntenic regions are depicted with colored boxes (Dataset S1, Table S3). The incongruence between the strain and T6SS phylogenetic trees indicate that most B. fragilis strains have acquired their T6SS through recent and independent horizontal transfer events. Examples of closely related strains acquiring distinct T6SSs (blue lines), distantly related strains acquiring similar T6SSs (red lines), and similar T6SSs encoding distinct putative E/I pairs (green lines) are shown.