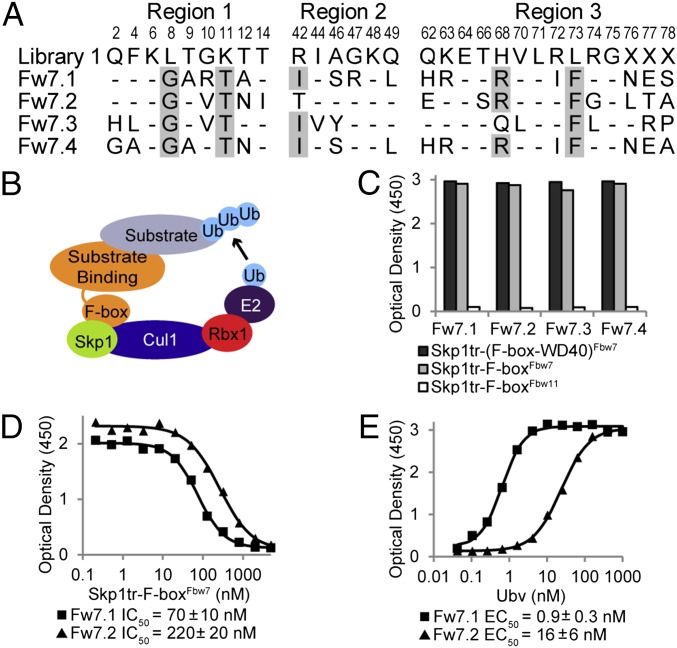
Fig. 1.
Ubvs selected for binding to the Skp1tr–Fbw7 complex. (B) Schematic of SCF E3 ligase. (A) Sequence alignment of selected Ubvs. Library 1 sequence is shown, where residue letters indicate the WT Ub sequence that was soft randomized and “X” denotes positions that were completely randomized. Only diversified positions are shown and residues in Ubvs conserved as WT Ub are indicated by dashes. Sequences showing conservation across selected Ubvs are highlighted in gray. (C) Binding of selected Ubvs to Skp1tr in complex with F-box–WD40Fbw7, F-boxFbw7, or F-boxFbw11. Ubv-phage binding was measured by ELISA with the indicated immobilized proteins. (D and E) Binding of purified Ubv.Fw7.1 or Ubv.Fw7.2 to Skp1tr–F-boxFbw7 as measured by ELISA. Data from a typical experiment are shown and the binding values are represented as mean ± SE of at least two experiments. (D) IC50 values were calculated by competitive ELISA as the concentration of Skp1tr–F-boxFbw7 in solution that blocked 50% of Ubv binding to immobilized Skp1tr–F-boxFbw7. (E) EC50 values were calculated by direct-binding ELISA as the concentration of Ubv at which 50% of the saturation signal is achieved for binding to immobilized Skp1tr–F-boxFbw7 complex.