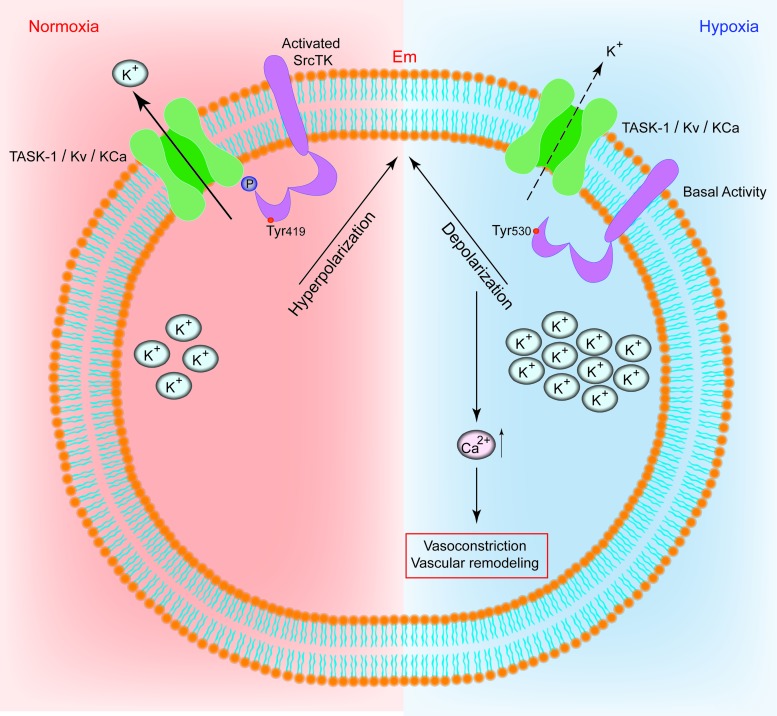
FIG. 6.
Schematic representation of the t-PMET. Scheme of the proposed interplay between potassium channels and c-Src in human PASMCs. Under normoxia, the phospho-Src (active-Src, phosphorylated at Tyr419) binds to TASK-1 channels, resulting in functional TASK-1 channels. Active TASK-1 channels maintain negative resting potential in hPASMCs. In hypoxia, the phospho-Src (active-Src) is decreased. Closed potassium channels result in depolarization and increased intracellular calcium levels. (+) Indicate increase and (−) indicate decrease. Em, resting membrane potential; KCa, calcium-dependent potassium channel; Kv, voltage-gated potassium channel; PASMC, pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells; TASK-1, TWIK-related acid-sensitive potassium channel-1. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars