Figure 3. γKlotho is necessary for TNBC cell survival and clonogenic growth.
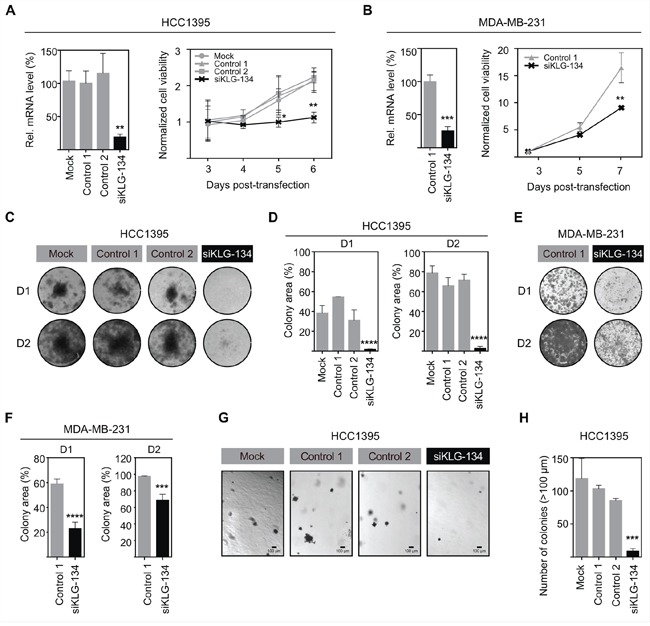
A. siRNA knockdown of γKlotho decreases the viability of HCC1395 cells. γKlotho expression in TNBC HCC1395 cells was knocked down by a pool of 3 siRNAs (siKLG-134) and the efficiency of γKlotho knockdown confirmed by qRT-PCR. mRNA levels are presented relative to control. **p ≤ 0.01; one-way ANOVA. 48 hours after transfection, cells were seeded and cell viability was monitored for 4 days by MTS assay. 12 hours post seeding-viability was used for normalization. Means of three independent experiments ± SD are presented. *p ≤ 0.05 **p ≤ 0.01; two-way ANOVA. B. siRNA knockdown of γKlotho decreases the viability of MDA-MB-231 cells. Mean of two independent experiments ± SD are presented. **p ≤ 0.01; two-way ANOVA. C, E. Knockdown of γKlotho inhibits liquid colony formation of HCC1395 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Cells were seeded in triplicates in 12-well plates at two different densities (D1=1000cells/well, D2=5000 cells/well). Ten (D2) and fourteen (D1) days after plating, colonies were stained with crystal violet and photographed. Representative images are shown. D, F. Liquid colony formation was quantified by determining the percentage of area covered by crystal violet stained cell colonies using ImageJ ColonyArea plugin. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three replicates. ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001; two-way ANOVA. G. Knockdown of γKlotho inhibits the anchorage-independent growth on soft agar of HCC1395 cells. Cells were transfected with a siRNA pool against γKlotho (siKLG-134) and corresponding controls and after 48 hours plated for anchorage-independent growth in soft agar. Representative images for each condition are presented. H. Colonies greater than 100 μm across their widest point were counted. Bars demonstrate average ± SD across triplicates. ***p ≤ 0.001, one-way ANOVA.
