Figure 4. The growth inhibitory effect of γKlotho knockdown is specific.
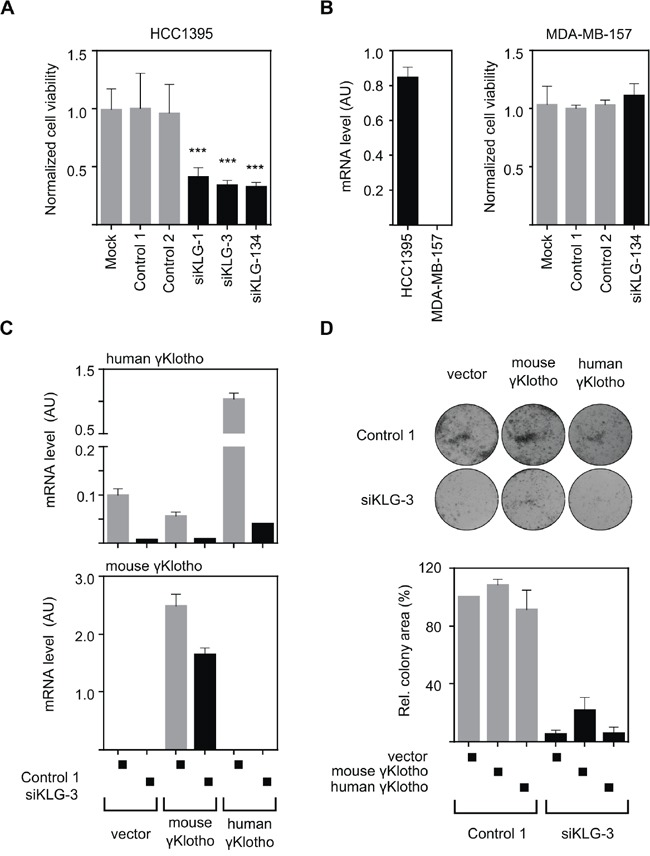
A. Two individual γKlotho siRNAs (siKLG-1 and siKLG-3) decrease HCC1395 cells viability to a similar extent as the siRNA pool (siKLG-134). Cell viability was determined by MTS assay 5 days after transfection. Means ± SD of 4 wells are shown. *** indicates p ≤ 0.001. B. γKlotho negative MDA-MB-157 cells (as assessed by qRT-PCR-left pannel) are not affected by γKlotho siRNA. Cell viability was assessed as in panel A. C. Mouse γKlotho is partially resistant to siKLG-3. HCC1395 cells stably overexpressing mouse or human γKlotho-Flag protein were transfected with siRNA and mRNA levels for mouse and human γKlotho determined by qRT-PCR. Data represent mean of three replicates ± SD. D. The siRNA-resistant mouse γKlotho gene in part rescues HCC1395 cells after γKlotho knockdown. HCC1395 cells stably overexpressing mouse or human γKlotho-Flag proteins were transfected with siKLG-3 against human γKlotho, 2 days later plated in 12-well plate (5000 cells/well) and cultured for 10 days. Representative images of colony formations are shown. Cell growth was quantified by determining the percentage of area covered by crystal violet stained cell colonies using ImageJ ColonyArea plugin and is presented relative to control. Data are presented as mean of three independent experiments ± SD.
