Figure 1. Detection of phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (pERK) and protein kinase B (pAkt) in hepatocellular carcinoma.
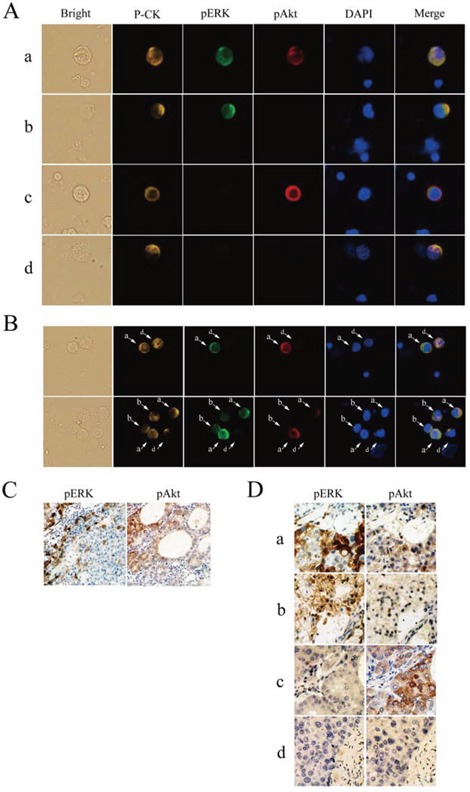
A. Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) stained for pan-cytokeratin (P-CK) (yellow), pERK (green), pAkt (red), and costained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue) (400× magnification). B. Coexistence of CTCs with various patterns of pERK/pAkt in the same field of view detected by multicolor immunofluorescence staining (200×). C. Immunohistochemical staining for pERK and pAkt in an individual cancer tissue (100×). D. Immunohistochemical staining for pERK and pAkt in serial sections of hepatocellular carcinoma tissues (200×); a, pERK+/pAkt+; b, pERK+/pAkt−; c, pERK−/pAkt+; d, pERK−/pAkt−.
