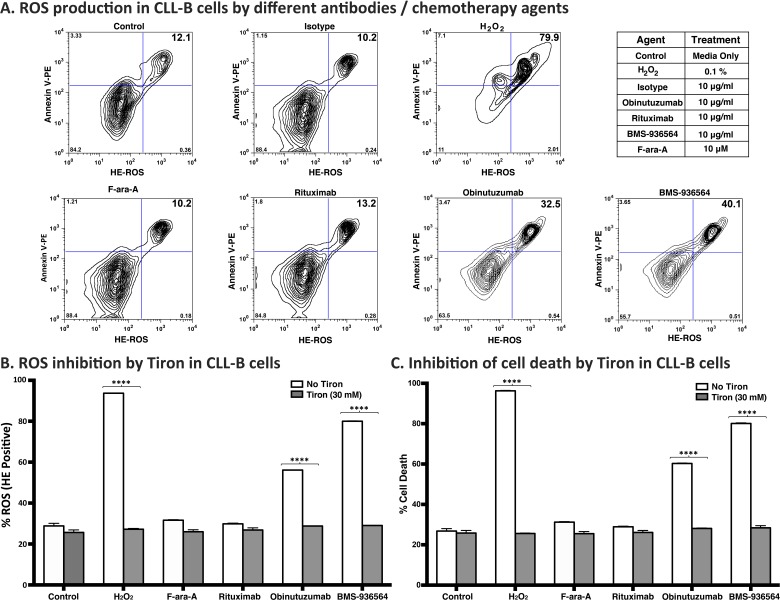
Figure 7. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) mediated mechanism of cell death by BMS-936564 in patients' derived CLL cells.
A. Primary CLL cells derived from patients were treated for 4 hrs either with 0.1% H2O2, 10 ug/ml of obinutuzumab, Rituximab, Ulocuplumab (BMS-936564) antibody or F-ara-A at the indicated concentrations. ROS production and cell death were assessed by flow cytometry. ROS+/Annexin-V+ double positive cells indicate the population of cell undergoing cell death with concurrent release of ROS (Upper right quadrant). Cells incubated in media only serve as base line control. This experiment represents typical data from three separate experiments conducted with duplicates per each incubation condition. B. The cells were incubated alone with Tiron (30 mM) or 10 μg/ml of either rituximab, obinutuzumab, Ulocuplumab (BMS-936564), 0.1% of H2O2 and 10 μM Fludarabine (F-ara-A) with 30 mM of Tiron for 4 hrs at 37°C. To measure ROS production, following CD19/CD5 labeling, cells were labeled with hydroxyethidium dye and incubated for 20 minutes at room temperature followed by flow cytometry analysis. The data presented represent mean ROS production± S.D. C. The cells were incubated alone with Tiron (30 mM) or 10 μg/ml of either rituximab, obinutuzumab, Ulocuplumab (BMS-936564), 0.1% of H2O2 and 10 μM Fludarabine (F-ara-A) with 30 mM of Tiron for 4 hrs at 37°C. TheThe percentage (%) cell death was measured using CD19/CD5/Annexin-V labeling followed by flow cytometry analysis. The representative data for ROS and % cell death has been shown from the same patient. The data presented represent mean ROS production± S.D.