Figure 5. Melatonin enhanced the berberine-mediated inhibition of p50/COX-2 signaling.
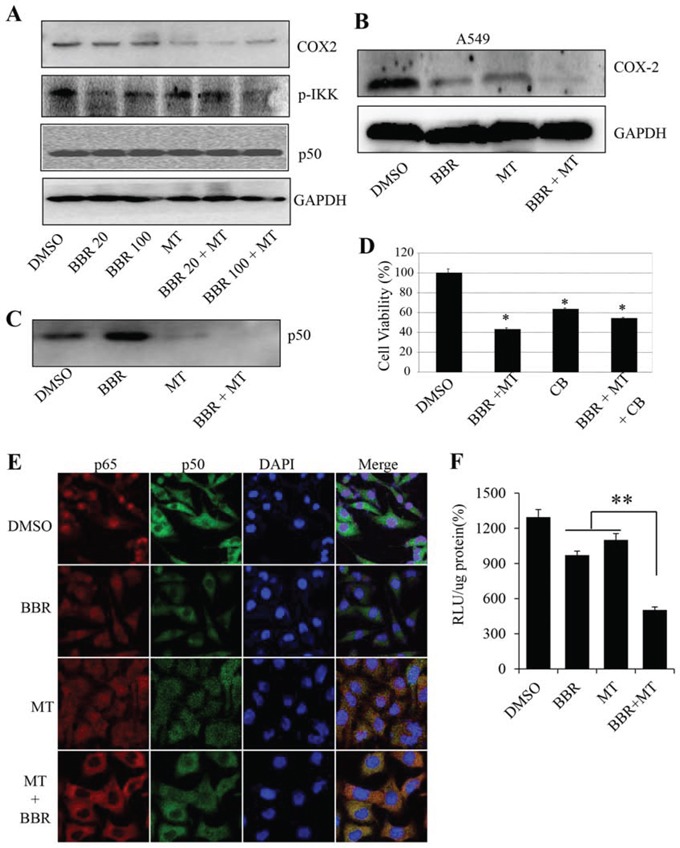
A. Human H1299 cells were treated with melatonin (MT, 1.0 mM) and berberine (BBR, 20 μM and 100 μM). At 48 hours after treatment, the p-IKK, COX-2 and p50 proteins (A) were analyzed by Western blotting. GAPDH were used as controls for sample loading. B. Human A549 cells were treated with melatonin (MT, 1.0 mM) and berberine (BBR, 50 μM). At 48 hours after treatment, the COX-2 protein was analyzed by Western blotting. C. H1299 cells were pretreated with the COX-2 selective inhibitor celecoxib (CB) (20 μM) for 24 hours, and then treated with melatonin (MT, 1.0 mM) and berberine (BBR, 100 μM). At 48 hours after treatment, cell viability was determined by MTT analysis. The percent cell viability in each treatment group was calculated relative to cells treated with the vehicle control. D. H1299 cells were treated with melatonin (MT, 1.0 mM) and berberine (BBR, 100 μM). At 48 hours after treatment, the binding of p50 to COX-2 promoter probe was analyzed by a streptavidin-agarose pulldown assay. E. H1299 cells grown on chamber slides were treated with melatonin melatonin (MT, 1.0 mM) and berberine (BBR, 100 μM). At 48 hours after treatment, the subcellular localization of p50 and p65 was examined by a confocal microscope. More than 100 cells were inspected per experiment, and cells with typical morphology were presented. F. H1299 cells were treated with melatonin (MT, 1.0 mM) and berberine (BBR, 100 μM) after transfection with COX-2 promoter-driven luciferase plasmids. The luciferase activity was detected by luciferase reporter assay kit. The data are presented as the mean ± SD of three separate experiments. *P < 0.05, significant differences between treatment groups and DMSO control groups.
