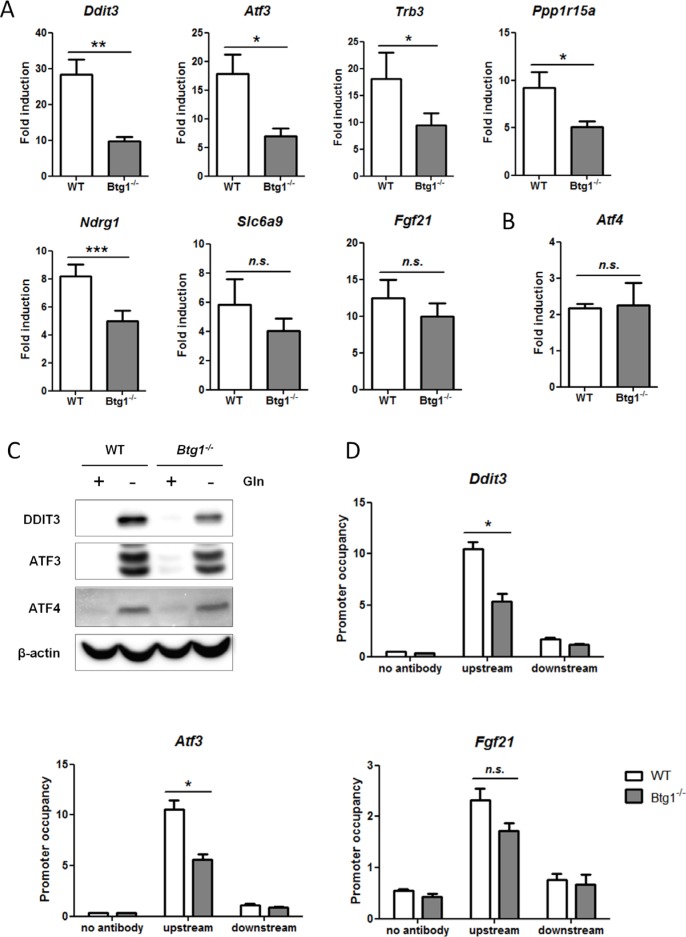
Figure 2. Loss of BTG1 negatively affects ATF4-mediated gene expression.
(A) Reduced expression of ATF4 target genes in Btg1−/− cells upon glutamine depletion. WT and Btg1−/− MEFs were stressed with glutamine starvation for 16 hours and qPCR was performed to measure the expression level of the seven ATF4 targets identified by gene expression analysis (Table 3). Data is presented as fold induction of mRNA (expression level of untreated samples were set to 1). Bars represent average data from four independent experiments ± SEM. P-values are indicated with ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05 (two-tailed paired t-test). (B) The expression level of Atf4 itself is not affected by the absence of Btg1. (C) The expression of ATF4 target genes in Btg1−/− cells is also attenuated at protein level. Western blot shows the protein expression of two ATF4 targets following glutamine starvation. (D) ATF4 occupancy on target gene promoters is affected by loss of BTG1. WT and Btg1−/− MEFs were stressed by glutamine starvation for 16 hours and ChIP was performed using an ATF4 antibody to determine ATF4 binding on the promoters of Ddit3, Atf3 and Fgf21. IP without antibody served as negative control. For each target gene, qPCR was performed using primers which recognize the ATF4 binding site (upstream) and a control region around 1.5 kb further (downstream). Bars represent average data from three independent experiments ± SEM. P-values are indicated with *P < 0.05 (two-tailed paired t-test).