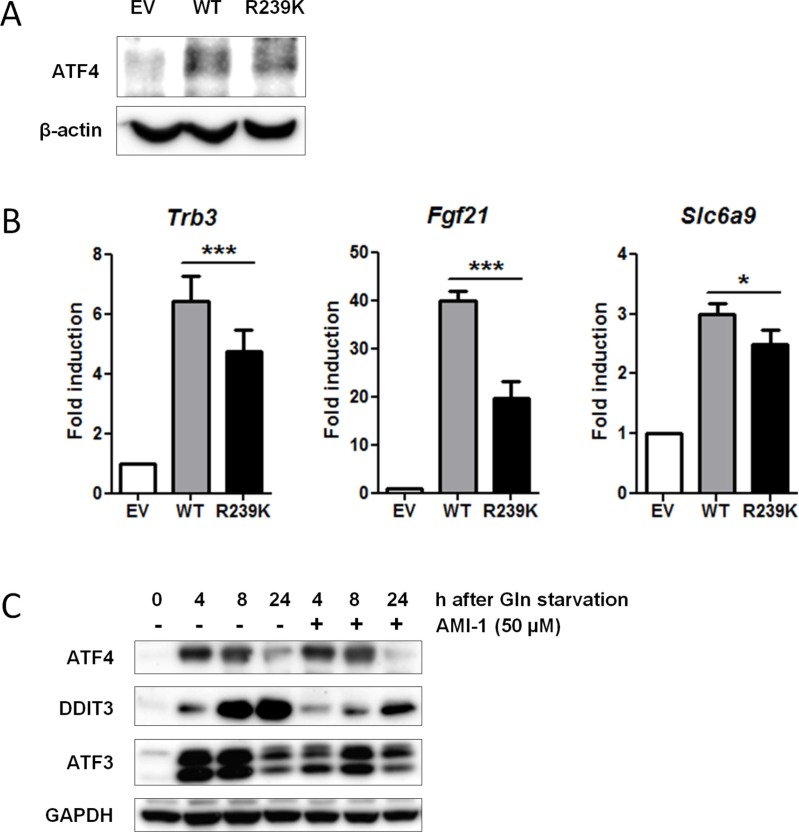
Figure 4. Loss of PRMT1-mediated methylation at residue R239 attenuates ATF4 function.
(A) Both WT and ATF4-R239K are equally expressed. Non-methylated ATF4-R239K was generated by overlap extension PCR (see Materials and Methods). WT and ATF4-R239K as well as an empty vector (EV) were retrovirally transduced into immortalized Atf4−/− MEFs. Protein lysates were generated and subjected to IP with ATF4Ab. Immunoblot demonstrates expression of ATF4. β-actin levels were used as a loading control. (B) ATF4 methylation potentiates its activity. EV, ATF4-WT and ATF4-R239K complemented MEFs were subjected to qPCR to determine expression of ATF4 targets identified by gene expression analysis (Table 3). Data are presented as fold induction of mRNA (expression level of untreated EV MEFs were set to 1). Bars represent average data from four independent experiments ± SEM. P-values are indicated with ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05 (two-tailed paired t-test). (C) WT MEFs were treated with 50 μM AMI-1 in the presence and absence of glutamine and western blot was performed for several ATF4 targets. GAPDH levels were used as a loading control.