Figure 2. Role of p53 and the RB family proteins in irradiation-induced downregulation of EZH2 expression.
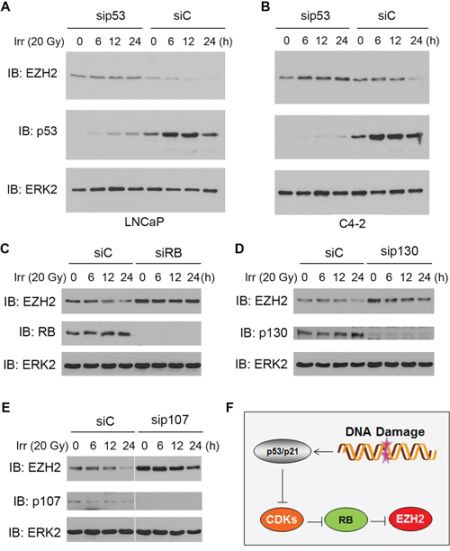
A–B. androgen-sensitive LNCaP (A) and castration-resistant C4-2 (B) cells were transfected with a pool of non-specific control siRNAs (siC) and p53-specific siRNAs. At 48 h after transfection cells were treated with γ irradiation, and cells were harvested at different time points for western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies. C–E. LNCaP cells were transfected with a pool of non-specific control siRNAs (siC) or RB-specific siRNAs (C), p130-specific siRNAs (D), or p107-specific siRNAs (E) At 48 h after transfection cells were treated with γ irradiation, and cells were harvested at different time points for western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies. ERK2 was used as a loading control. F. a hypothetical model depicting the causal role of p53 and RB in conventional chemotherapy (CPT) and radiotherapy (both are DNA damage-based therapeutics)-induced downregulation of EZH2 in PCa cells.
