Figure 1.
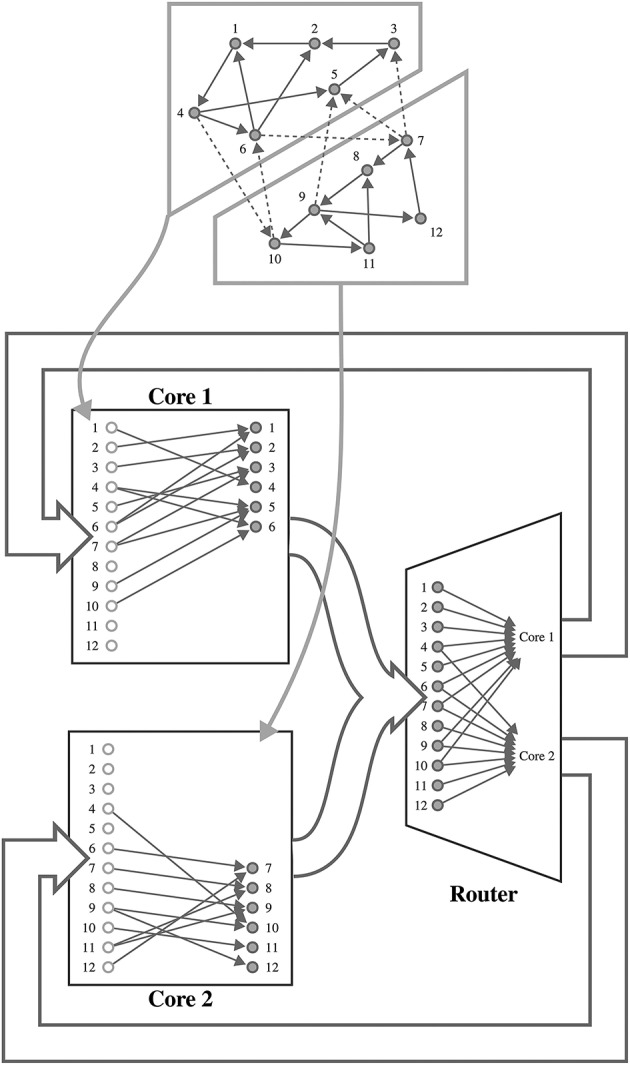
Mapping of a spiking neural network to SpiNNaker. For example a network consisting of 12 neurons is distributed between two SpiNNaker cores. Each core is responsible for simulating six neurons (filled circles) and holds a list of afferent synapses (non-filled circles) associated with each neuron in the network. The SpiNNaker router routes spikes from firing neurons (filled circles) to the cores responsible for simulating the neurons to which they make efferent synaptic connections.
