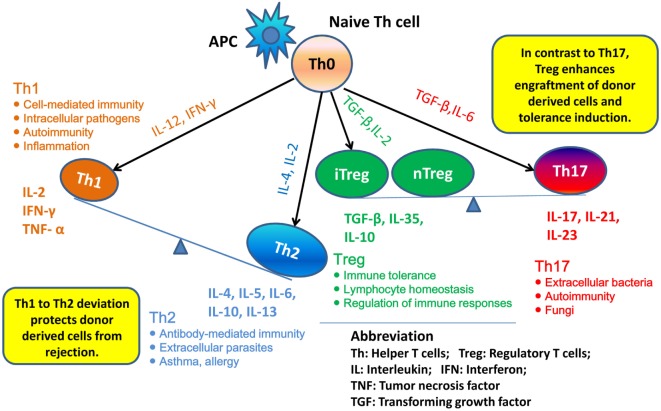
Figure 1.
Th1 to Th2 deviation and Th17–Treg axis. Following activation by antigen-presenting cells (APCs), naive Th cells can be polarized into different effector T cell subsets: T helper 1 (Th1), Th2, Th17, and induced regulatory T (iTreg) cells, depending on the local cytokine environment. Besides iTreg, there is another Treg subset, “natural” Treg (nTreg), which develops as a distinct lineage in the thymus. In neonatal mice, newborn T cells generate Th2-biased immune response, thus may protect donor cells from rejection. nTreg and iTreg are critical in the mechanism of neonatal tolerance induction. They promote the donor cells engraftment and tolerance induction. By contrast, promotion of Th17 immunity can prevent establishment of lymphoid chimerism and neonatal tolerance induction.