Figure 6.
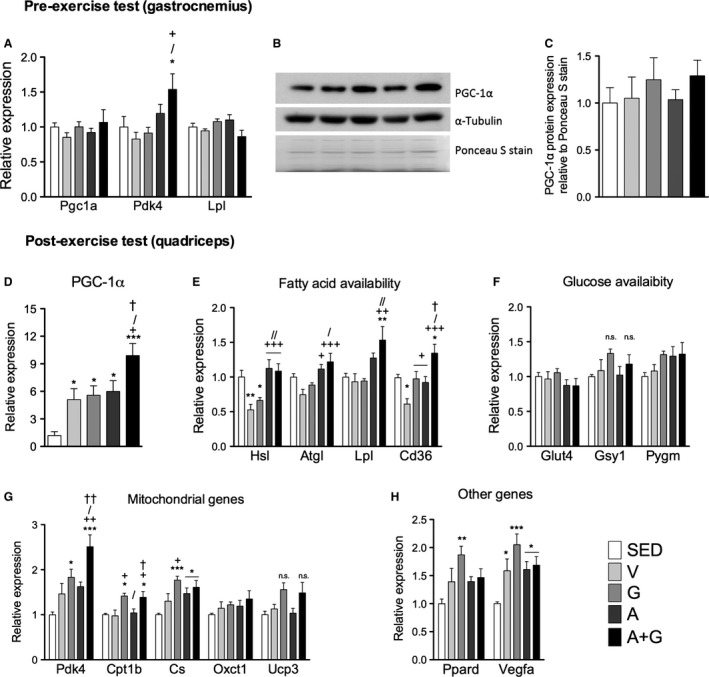
Combined pharmacological AMPK and PPARδ activation influences gene expression of substrate utilization related genes in skeletal muscle in trained mice. Pre‐exercise test (A) Pgc1a, Pdk4 and Lpl expression and, (B) representative immunoblot image of PGC‐1α and α‐Tubulin, and Ponceau S digitized image, and (C) relative PGC‐1α protein expression in gastrocnemius muscle. Post‐exercise test messenger RNA expression of (D) PGC‐1α and genes related to (E) fatty acid availability, (F) glucose availability, (G) mitochondrial oxidative metabolism, and (H) Ppard and Vegfa were measured. For mRNA expression, data were normalized to Hprt expression while for protein expression, data were normalized to total Ponceau S signal. Data were rationalized to SED, and expressed as means ± SEM (pre‐exercise test n = 6, postexercise test n = 7–9). Significant differences were analyzed by one‐way ANOVA followed by Newman‐Keuls multiple comparison test. Asterisk (*), plus sign (+), slash (/) and dagger (†) represent significant difference relative to SED, V, G and A, respectively. Single symbols, P < 0.05; double symbols, P < 0.01; while triple symbols, P < 0.001.
