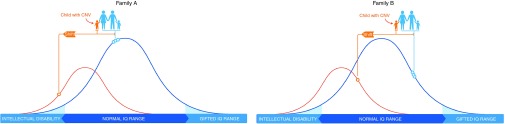
Figure 2.
The blue curve represents the normal distribution of intelligence quotient (IQ) in the general population. The smaller, orange curve shows the IQ distribution for individuals with a particular copy-number variant (CNV). Circles on each curve indicate IQ scores for specific family members. In both family A and family B, this CNV confers the same magnitude of deleterious impact (“shift”) on a child's IQ. In family A, the CNV shifts the affected child's IQ into the range of intellectual disability. In family B, because the family IQ starting point is higher, the CNV shift does not reach the defined threshold for intellectual disability. Even in family B, however, the shift has an effect, lowering the child's IQ from where it would have been without the CNV.