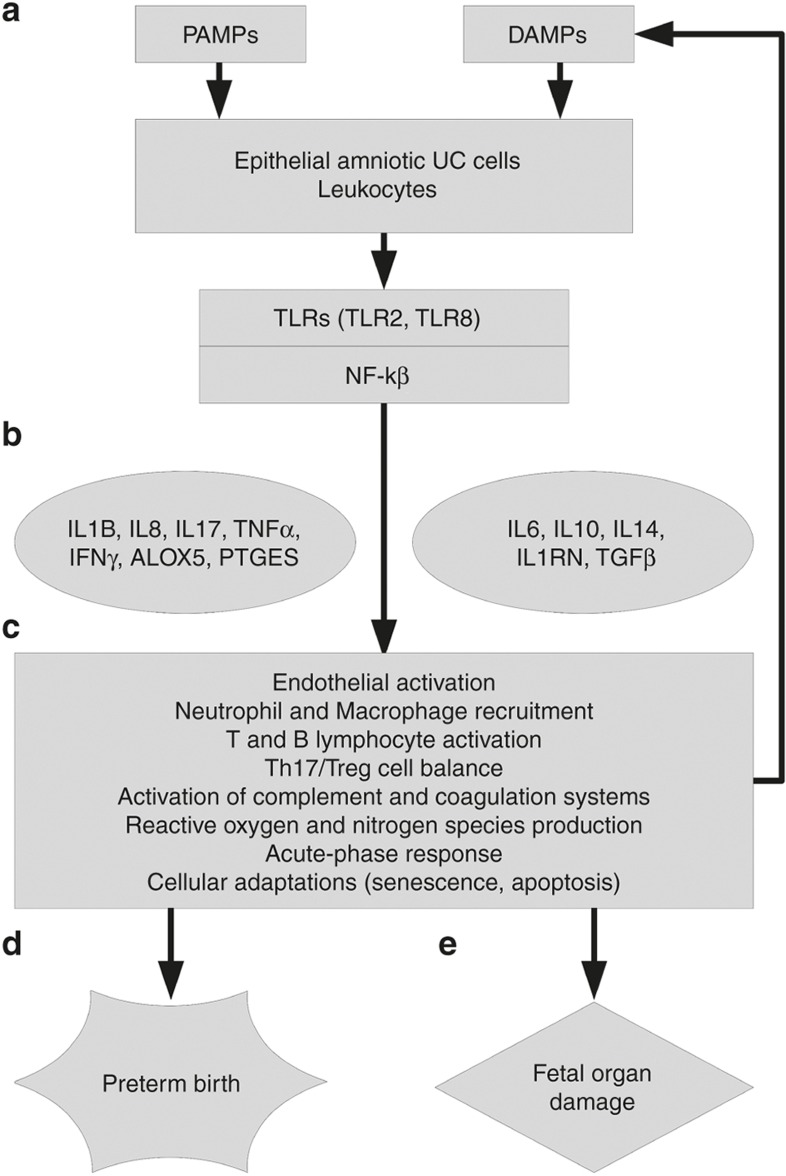
Figure 3.
Molecular architecture of FIR. (a) UC microbial invasion is detected by epithelial amniotic cells and leukocytes in UC tissue. TLRs identify PAMPs, and DAMPs, producing and enhancing FIR and participating in the activation of the NF-kB signaling pathway. (b) The transcriptional response of NF-kB activates proinflammatory mediators and anti-inflammatory ones. (c) The state of multiple cell types and tissues is affected by the acute inflammatory cascade. (d) The activation of proinflammatory pathways can trigger the production of labor intermediates and promote parturition onset. (e) The acute inflammatory response can damage fetal organs through its mediators and immune cells.