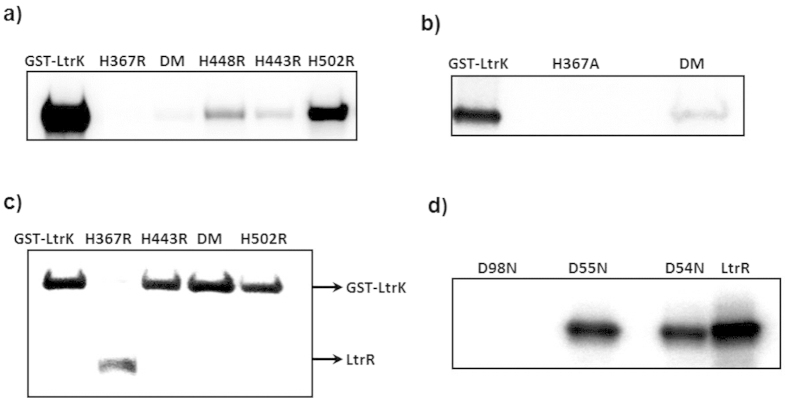
Figure 3. Effects of mutations on the phosphorylation activities of LtrK and LtrR.
To assess the phosphorylation state of proteins, samples were electrophoresed on a SDS-polyacrylamide gel, and autoradiography performed by phosphorimaging (panels a–d). (a) Autophosphorylation of LtrK mutant proteins. Proteins (7 μg) were incubated with [γ-32P]-ATP at room temperature for 30 min. Histidine residues were replaced with arginine, including the double mutant (DM) H443R/H448R. (b) Autophosphorylation of LtrK mutant proteins. Histidine residues were replaced with alanine, including the double mutant (DM) H443A/H448A. (c) Phosphatase activity of LtrK mutant proteins. LtrR-P was incubated with wild-type (lane 1) and mutant proteins H367R (lane 2), H443R (lane 3), H443R/H448R (lane 4), H502R (lane 5) for 30 min at room temperature. (d) Phosphotransfer from LtrK-P to LtrR mutant proteins. LtrR (80 μg) wild-type and mutant proteins were phosphorylated by GST-LtrK-P (20 μg) immobilized on a gravity flow column containing glutathione agarose beads as described for Fig. 2c.