Figure 1.
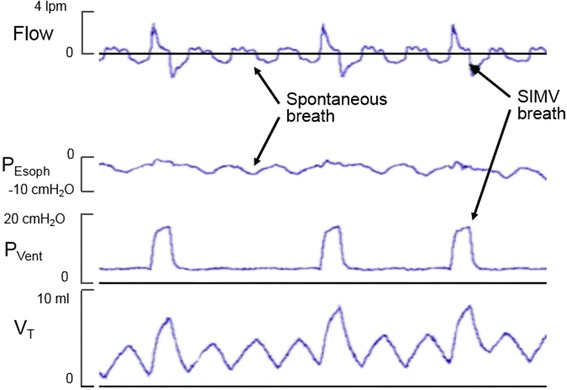
Synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation. Tracings of flow, esophageal pressure (PEsoph), ventilator pressure (PVent) and tidal volume (VT) obtained from a premature infant undergoing SIMV. The interval between SIMV cycles is adjusted by the ventilator to maintain synchrony with the infant’s inspiratory efforts (negative deflections in the esophageal pressure). The combination of the positive pressure and the infant’s spontaneous inspiratory effort achieve a larger tidal volume than that of the non-assisted spontaneous breaths.
