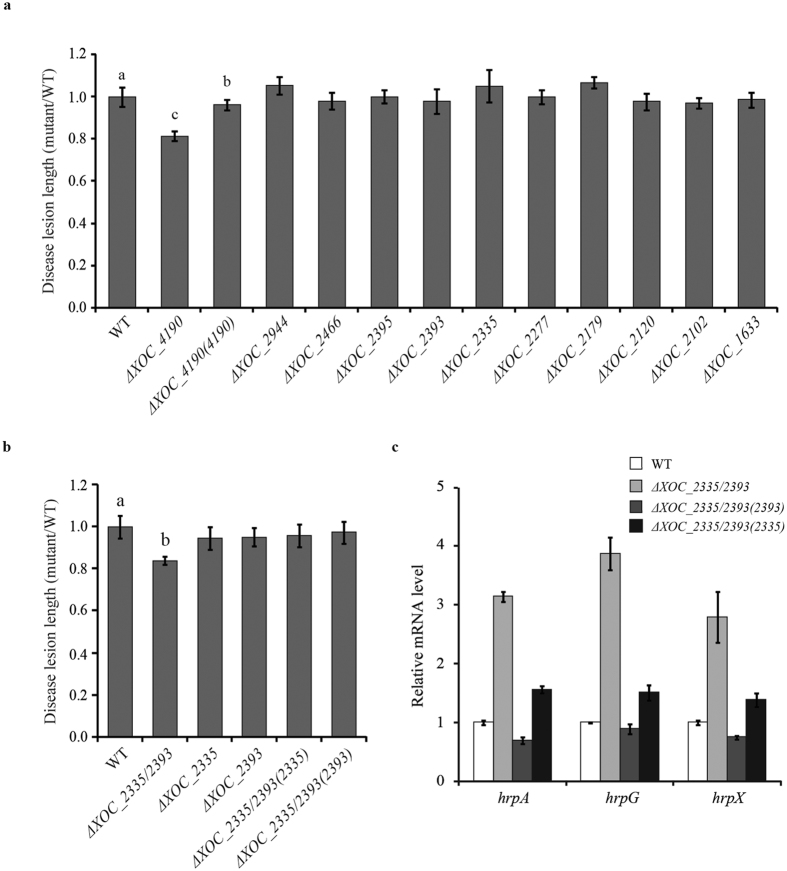
Figure 3. The effects of mutation of GGDEF-EAL protein-encoding genes on virulence of X. oryzae pv. oryzicola to rice.
(a) The lesion length on the ΔXOC_4190-inoculated leaves of rice cv. Shanyou 63 was significantly shorter than that caused by the wild-type strain. Virulence of the ΔXOC_4190 mutant was restored by the plasmid-borne full-length XOC_4190 gene. Other single-gene deletion mutants have no altered virulence to rice compared with the wild type. (b) The lesion length caused by the ΔXOC_2335/XOC_2393 double mutant was significantly shorter than that caused by the wild-type strain. Both XOC_2335 and XOC_2393 can restore virulence of the double-gene deletion mutant to the wild-type level. The length of disease lesions was measured at 14 d after pressure inoculation of the wild-type, mutant and complemented strains, respectively. The ratios of disease lesion length caused by the mutant strains to that caused by the wild-type strain were shown. Data are presented as means ± SE. The letters (a,b) indicate significant difference (P < 0.05) by Duncan’s multiple range test. (c) The effect of double-gene deletion of XOC_2335 and XOC_2393 on the expression of hrp genes in Xoc. Expression of hrpA, hrpG and hrpX in the wild-type (WT), ΔXOC_2335/2393, ΔXOC_2335/2393(2393), ΔXOC_2335/2393(2335) strains was detected by qRT-PCR. 16S RNA was used as an internal control for data analyses. A significant increase of hrpA, hrpG and hrpX mRNA expression was detected in ΔXOC_2335/2393 compared with the wild-type and complementation strains.