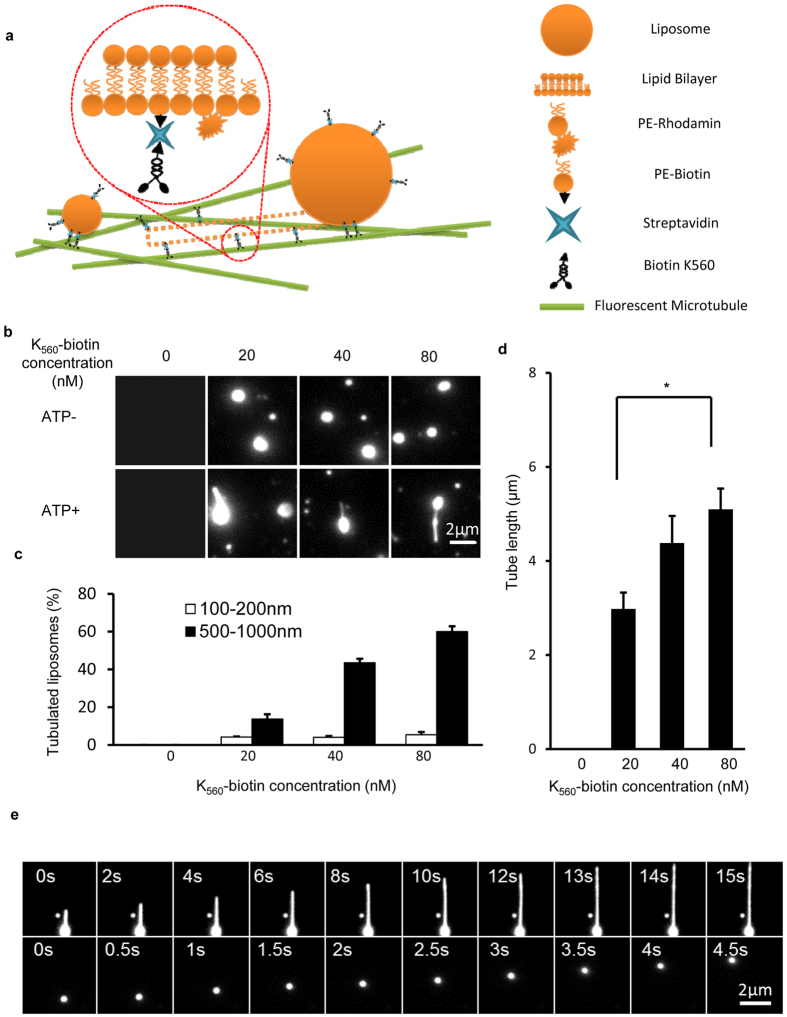
Figure 3. Size dependent liposome motion and tubulation driven by truncated KIF5B in vitro.
(a) Schematic diagram of the in vitro liposome tubulation assay. The brain polar lipid mixture was supplemented with 20% PE-biotin and 1% PE-rhodamine B, and the solution was extruded through a 100 nm or 1000 μm pore polycarbonate filter to generate different size liposomes. K560-biotin was mixed with streptavidin and liposomes, and the resulting complexes were transferred into flow chamber channels pre-incubated with microtubules. Liposome tubulation was visualized in the presence of ATP. (b) The effect of K560-biotin concentration on in vitro liposome tubulation. Different concentrations of K560-biotin (0, 20, 40 and 80 nM) were prepared, mixed with streptavidin (1:1 molar ratio) and then incubated with liposome solution on ice. The liposome concentration was held fixed at 28 μg/ml. The resulting mixtures were transferred to flow chamber channels coated with microtubules, and images were collected with a Nikon TIRF microscope. Scale bar, 2 μm. (c) The percentage of tubulated liposomes in (b) was determined. n > 100 from three independent experiments. Error bars indicate the s.d. (d) Tube length from (b) was assessed and quantified. n > 100 from three independent experiments. Error bars indicate the s.d. (e) Time-lapse sequence of liposome (500–1000 nm) tubulation and liposome (100–200 nm) motion were collected in the presence of ATP. Scale bar, 2 μm.