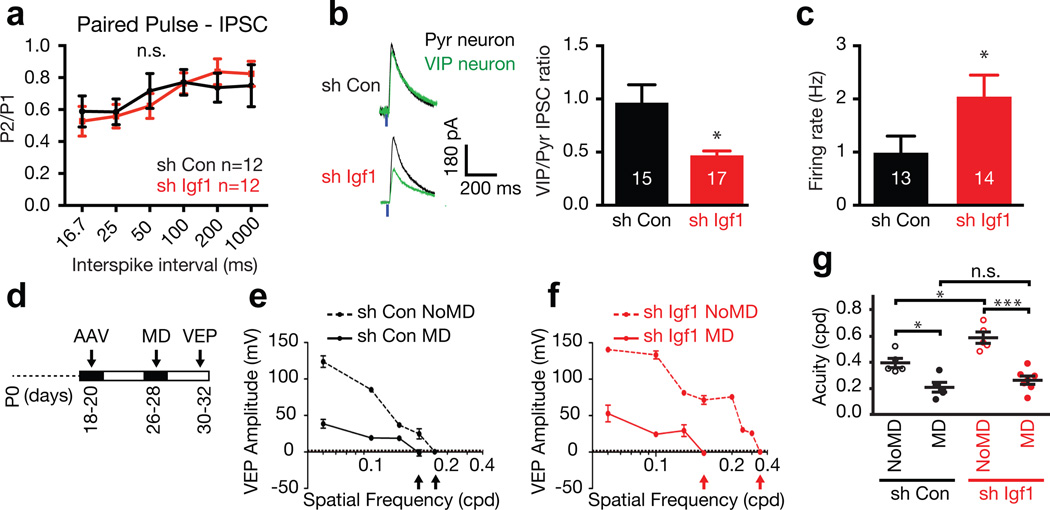
Figure 4. VIP neuron-derived IGF-1 regulates VIP neuron function and regulates visual acuity in an experience-dependent manner.
a) Paired-pulse recordings from VIP neurons infected with control or Igf1 shRNA (p = 0.96, two-way ANOVA).
b) Left: average traces of light-evoked IPSCs (eIPSC) from paired recordings of VIP neurons infected with control or Igf1 shRNA (green traces) and neighboring pyramidal neurons (black traces). Right: quantification of eIPSC amplitude of the VIP neuron after infection with AAVs expressing control or Igf1 shRNA normalized, to the eIPSC amplitude of the paired pyramidal neuron (p = 0.01, Mann-Whitney U-Test).
c) Average firing rate of VIP neurons infected with Igf1 or control shRNA (p = 0.04, Mann-Whitney U-Test).
b, c) Numbers inside bars indicate the number of cells recorded
d) Schematic of the schedule for monocular deprivation (MD) experiments. e–f) Representative traces of visually evoked potential (VEP) amplitude as a function of spatial frequency (cpd) in the contralateral visual cortex of mice that received bilateral injections of AAVs expressing Igf1 or control shRNA into their visual cortices and were subjected to MD or not.
g) VIP neuron-derived IGF-1 restricts visual acuity in an experience-dependent manner. Visual acuity in mice injected with AAVs expressing Igf1 or control shRNA with no MD or MD (P24 – P28; control shRNA NoMD, n = 5; control shRNA MD, n = 5; Igf1 shRNA NoMD, n = 5; Igf1 shRNA MD, n = 7; p* < 0.05, p*** < 0.0001, n.s. – not significant, One way ANOVA-Tukey post test).