Fig. 6.
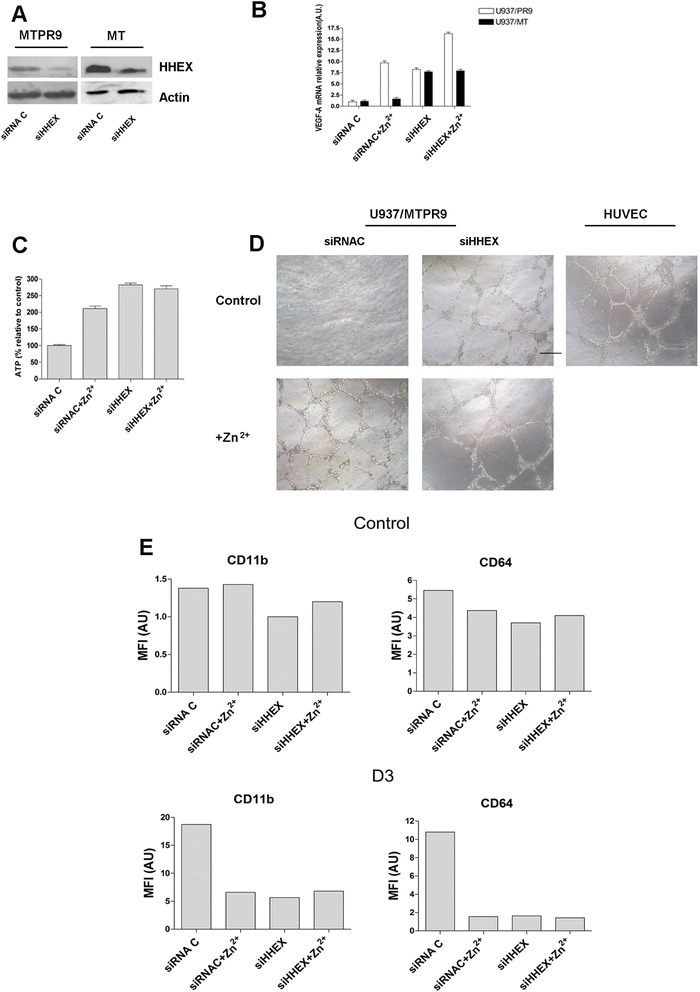
a, b, c Effect of HHEX silencing on cell proliferation and VEGF-A expression by PR9 cells. MT or PR9 cells have been treated either with a control siRNA or with a siHHEX RNA and then evaluated for HHEX expression by WB (a), VEGF-A mRNA expression by real-time PCR (b), and cell proliferation (c). d Effect of HHEX silencing on the capacity of PR9 cells to release pro-angiogenic growth factors. PR9 cells have been treated with a control siRNA or with siHHEX RNA and then grown for 48 h without (control) or with ZnSO4 (+Zn2+); cell supernatants were collected and assayed for their capacity to promote endothelial tube formation using an endothelial tube formation assay using HUVEC cells plated in Matrigel. As a positive control, HUVEC cells were plated in Matrigel in EGM2 complete medium containing exogenous angiogenetic growth factors. e Effect of HHEX silencing in the VitD3-induced cell differentiation of PR9 cells. PR9 cells were treated either with control siRNA or with siHHEX RNA and then grown for 3 days either in the absence (c) or in the presence of 100 μM ZnSO4 (Zn2+), either in the absence (control) or in the presence of 1α25OH-VitD3 (D3) for 72 h, harvested and then analyzed for the expression of CD11b and CD64 membrane markers by flow cytometry. The results of one representative experiment are reported in the figure
