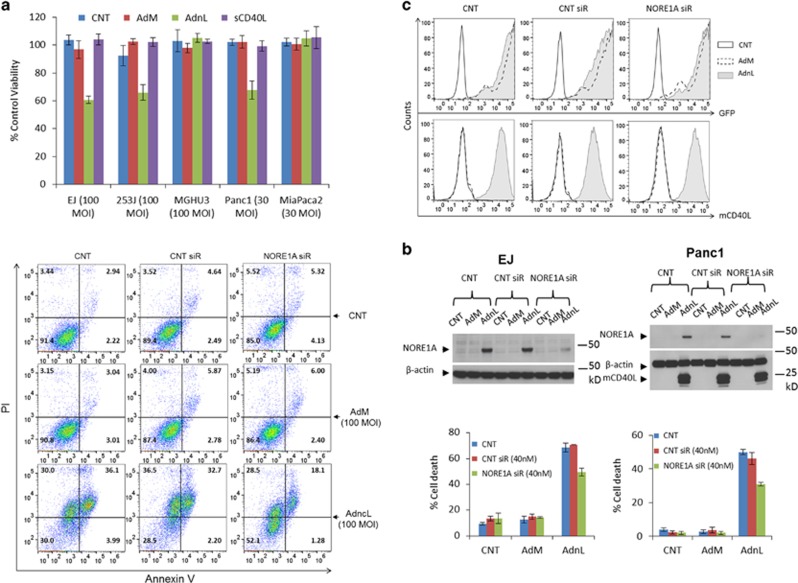
Figure 3.
Inhibition of mCD40L-induced NORE1A expression reduces CD40L-induced cell death. (a) The bladder carcinoma cell lines EJ, 253J and the CD40-negative MGHU3 cells and the pancreatic cell line Panc1 and the CD40-negative MiaPaca-2 cells were infected with 100 and 30 MOI of either RAdMock (AdM) or RAdnCD40L (AdnL), respectively, or left uninfected as a negative control (CNT) or treated with recombinant sCD40L at a final concentration of 1 μg/ml for 30 h. Cell viability was assessed by WST-1 assay. Results represent the mean of triplicate samples ±S.D. (b) EJ and Panc1 cells were transfected with 40 nM of either off-target siRNA or NORE1A siRNA or left untransfected as a negative control for 48 h. Cells were lightly trypsinzed and collected, followed by infection with 100 and 30 MOI, respectively, of either AdM or AdnL or left uninfected as a negative control for further 24 h. Cell death was then assessed by FACS analysis utilising the PI and annexin v staining method. Results represent the mean of triplicate samples ±S.D. NORE1A inhibition by NORE1A siRNA in AdnL-infected EJ or Panc1 cells was confirmed by western blot analysis, in addition to mCD40L and β-actin as a loading control. (c) Expression of mCD40L and GFP in EJ cells were examined by FACS analysis to ensure equal MOI infection between different treatments