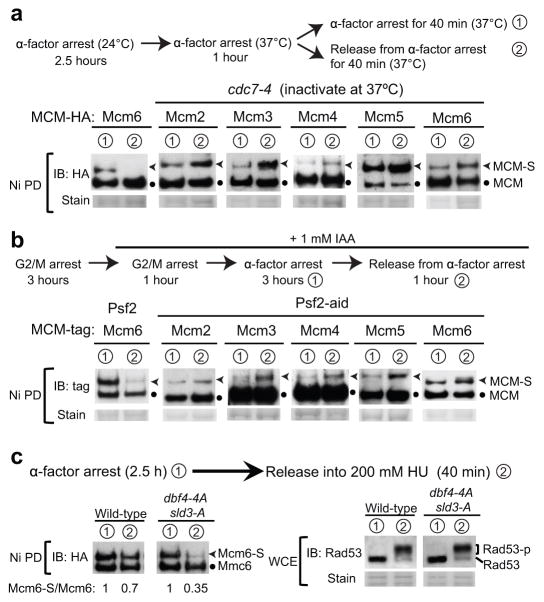
Figure 3. Mcm2–6 sumoylation loss at the G1-S transition requires DDK, GINS, and replication initiation.
a. Mcm2–6 sumoylation in G1 phase does not require DDK, but its decrease in S phase depends on DDK. Top: experimental schemes for Cdc7 inactivation as described previously38 (see Methods). The sumoylation status of each HA-tagged MCM at indicated time points is shown.
b. Sumoylation of Mcm2–6 in G1 phase does not require GINS, but its decrease in S phase depends on the GINS subunit Psf2. Top: experimental schemes for Psf2 depletion (see Methods). Mcm5 was tagged with Strep tag II to be compatible with the Psf2–aid construct, and other MCM subunits are tagged with HA.
c. Mcm6 sumoylation loss coincides with firing of both early and late origins. Top: experimental schemes for G1 arrest and release. Immunoblots show Mcm6 sumoylation status at indicated time points. Note that dbf4-4A sld3-A cells allow late origin firing under this condition12. Rad53 phosphorylation (bottom) shows the effectiveness of HU treatment.