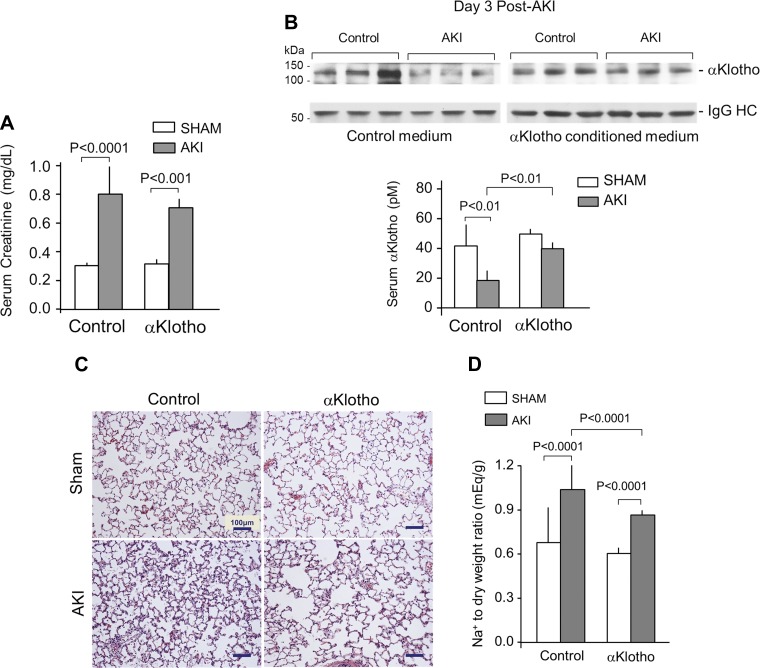
Fig. 1.
αKlotho deficiency and repletion in acute kidney injury (AKI). Sprague-Dawley rats underwent bilateral ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI), and lungs were harvested 3 days later. The control group underwent general anesthesia and laparotomy with manual manipulation of the kidneys but without IRI (Sham). Rats received intraperitoneal injection of either αKlotho-containing or control conditioned media 6 h after surgery. A: severity of AKI was measured by serum creatinine level in the animals 3 days after IRI. B: serum αKlotho level was measured by immunoprecipitation-immunoblot 3 days after IRI at the time of lung harvest. Representative blots are shown. IgG-HC, immunoglobulin heavy chain. C: representative lung histology (Trichrome stain). D: Na+ to dry weight ratio as a measure of interstitial edema. Means ± SD (n = 7–8 animals per group). Statistical significance was assessed by ANOVA.