Fig. 2. Intrinsic topography of pontine migratory stream and nuclei and Ezh2 dependent Hox regulation.
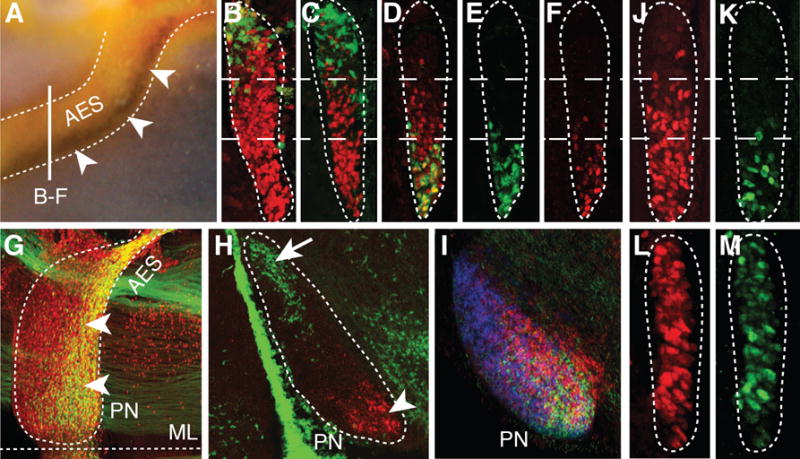
(A) Hoxb5/Barhl1 in situ hybridization on E15.5 whole-mount brain (lateral view). Arrowheads show Hoxb5+ neuron ventral restriction in anterior extramural stream (AES). (B to C) E15.5 r5–6::Cre;R26RZsGreen AES coronal sections co-stained with ZsGreen/Pax6 (red) (B) or ZsGreen/Hoxb4 (red) (C) showing complementary dorsal ZsGreen+/ventral Hoxb4+ cell distributions (bar in (A) shows section level). (D to F) E15.5 Hoxa5::Cre;R26RZsGreen AES sections showing partially overlapping ZsGreen/Hoxb4 (red) co-stainings with offset dorsal limits (D), while ZsGreen+ (E) and Hoxa5+ (F) neurons display similar ventral restriction. (G to H) E15.5 whole-mount Hoxa5::Cre;R26RZsGreen (G) or r5–6::Cre;R26RZsGreen (H) sagittal sections co-stained with ZsGreen/Pax6 (red) or ZsGreen/Hoxa5 (red), respectively, illustrating posterior pontine nuclei (PN) restriction of Hoxa5+ neurons (arrowheads, G,H), and anterior restriction of r6-derived neurons (arrow, H). (I) Hoxb3/Hoxb4/Hoxb5 nested in situ expression patterns on PN sagittal section (J to M) Hoxb4 (red) and Hoxa5 (green) immunostainings of E15.5 Wnt1::Cre;Ezh2fl/+ control (J,K) and Wnt1::Cre;Ezh2fl/fl mutant (L,M) AES. In (L,M), Hoxb4 and Hoxa5 loose their spatial restriction and are ectopically derepressed up to the dorsal edge of the AES. ML, ventral midline.
