Fig. 2. Mutant p53 expands the population of cells with stem-like properties.
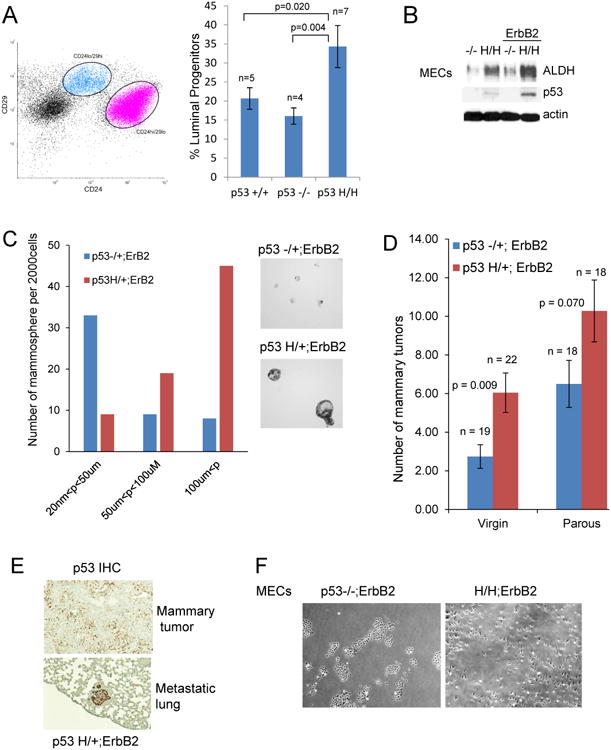
(A) Mutant p53 R172H promotes the expansion of luminal progenitors. Primary MECs isolated from mammary of wtp53, p53-/- and p53H/H mice are stained with CD61, CD24 and CD29. The luminal progenitor pool, defined by Lin- ;CD61+CD24high;CD29low. The presented data originates from MECs independently isolated from 7 p53 H/H mice, 4 p53-/- mice and 5 wtp53 mice.
(B) The presence of the mutant p53 allele increases ALDH+ levels in primary MECs in both straight p53H/H mice (lane 1, 2) and p53H/H;ErbB2 mice (lane 3,4) compared to p53 null littermates.
(C) The mutant p53 allele induces expansion of primary mammary epithelial stem cells in ErbB2 mice. Size comparison of mammospheres from MECs of p53H/+;ErbB2 vs p53-/+;ErbB2 mice (10×). Representative experiment shown.
(D) Parity induces higher tumor multiplicity in mice of both genotypes p53H/+;ErbB2 and p53-/+;ErbB2 compared to their virgin counterparts. Parous p53H/+;ErbB2 mice show the higher number of mammary tumors (10.3 tumors per mouse) compared to p53-/+; ErbB2 parous littermates (6.5 tumors per mouse).
(E) Mutant p53 is highly stabilized in lung metastasis compared to heterogeneous p53 staining in primary tumors from the same mouse. Representative image. Matching metastatic lungs/tumor specimens derived from 5 independent mice were analyzed. p53 IHC, 10×magnification.
(F) Mutant p53 allele changes cell morphology from epithelial in p53-/-;ErbB2 MECs to mesenchymal in H/H;ErbB2 MECs. 4× magnification.
