Figure 1.
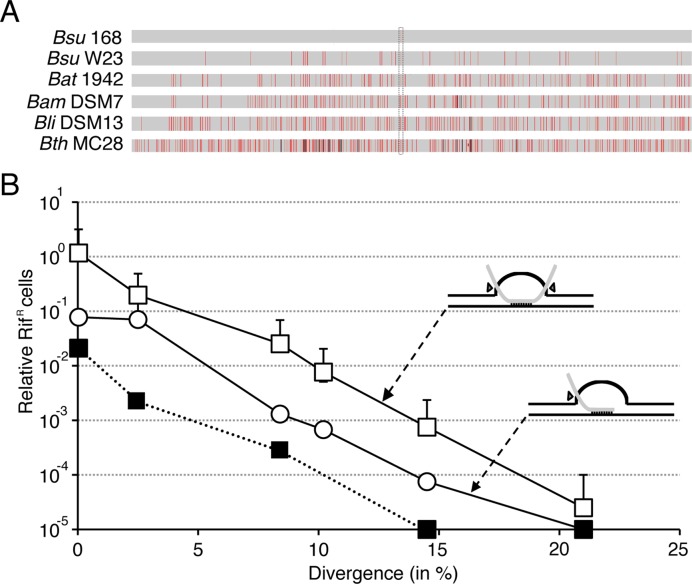
Average chromosomal transformation frequencies as a function of sequence divergence (in %) from recipient. (A) The rpoB482 DNA was derived from B. subtilis 168 (Bsu 168, 99.96% identity), B. subtilis W23 (Bsu W23, 97.53%), B. atrophaeus 1942 (Bat 1942, 91.65%), B. amyloliquefaciens DSM7 (Bam DSM7, 89.88%), B. licheniformis DSM13 (Bli DSM13, 85.48%) and B. thuringiensis MC28 (Bth MC28, 79.17%). The rpoB482 mutation, which confers resistance to rifampicin (RifR) is framed by dotted lines. Mismatches between RifR donor and the corresponding rpoB in the RifS recipient strain are indicated by vertical red bars and an insertion/deletions by vertical black bars. If two mismatches are located below the MEPS distance they count as a single red bar, the thickness of the bar represent the number of mismatches in the neighbourhood. (B) The undigested rpoB482 DNA (empty or filled squares) or linear SpeI-cleaved rpoB482 DNA (empty circle) was used to transform BG1359 (Δrok) (empty circles and squares) and its isogenic parental strain BG214 (filled squares) competent cells with selection for RifR. All values are means from 3 to 5 independent experiments. In the upper and lower inserts the black lines represent the recipient chromosomal DNA (a supercoiled molecule), and the grey line the homologous donor linear ssDNA. If the ssDNA was randomly linearized by the uptake machinery the transformation heteroduplex would form a double-ended D-loop structure (upper insert), but a one-ended D-loop would be observed if the DNA was in vitro linearized within the rpoB482 DNA (lower insert). The pointing triangles indicate the simultaneous incision (upper insert) or asynchronous incision (bottom insert) by a putative D-loop resolvase.