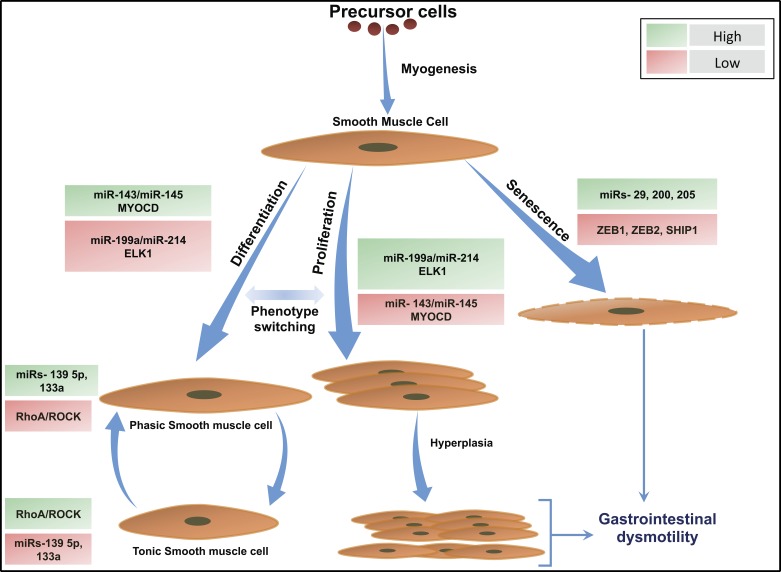
Fig. 2.
Role of miRNAs in the regulation of GI smooth muscle phenotype switch. Schematics illustrate miRNA-mediated GI smooth muscle switching into proliferative, differentiated, and senescent phenotypes. miRNAs 143/145 control GI SMC phenotype via targeting MYOCD whereas miRNAs 199a/214 target ELK1 and regulate GI SMC phenotype. Upregulation of miRNAs 143/145 and corresponding downregulation of miRNAs 199a/214 lead to differentiation of GI SMCs into a contractile phenotype (97). RhoA/ROCK levels correlate inversely with tissue expression of miRNAs 139 5p/133a in the GI SMCs, resulting in a phasic or tonic GI SMC phenotype (23, 121). Downregulation of miRNAs 143/145 and corresponding upregulation of miRNAs 199a/214 results in GI SMC proliferation that can progress into SMC hypertrophy culminating in GI dysmotility. Senescence of GI SMCs is mediated by miRNAs 29, 200, and 205 via targeting ZEB1, ZEB2, and SHIP1. Green boxes indicate high; red boxes indicate low. GI, gastrointestinal; MYOCD, myocardin; ROCK, rho kinase; SMC, smooth muscle cell; ZEB, zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox.