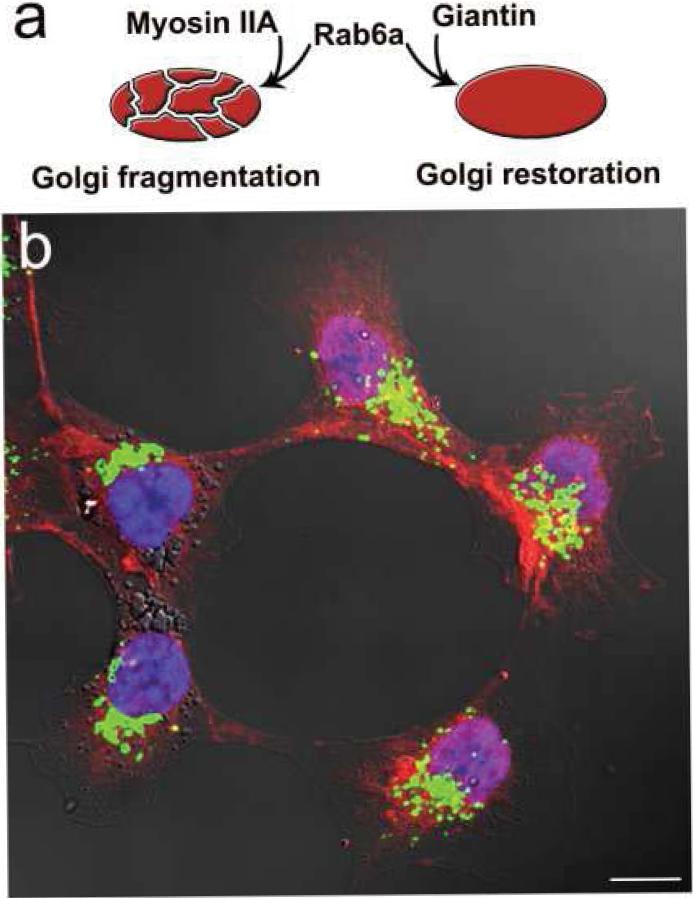
Figure 2.
The inhibition or knockdown of non-muscle Myosin IIA (NMIIA) results in restoration of compact Golgi in prostate cancer cells. (a) Giantin and NMIIA compete for Rab6a. In advanced prostate cancer, Rab6a and NMIIA associate to form fragmented Golgi phenotype. Cessation of NMIIA induces tight cooperation of Rab6a and giantin followed by dimerization of latter and formation of compact Golgi. (b) Confocal fluorescence photograph (64×; bars, 10 μm) of DU145 prostate cancer cells treated with Blebbistatin, an inhibitor of NMIIA, and stained for a Golgi marker giantin (green), polylactosamine stained with Lycopersicon esculentum agglutinin lectin (red), and nucleus with DAPI (blue). Restoration of compact Golgi morphology is accompanied by Golgi targeting of a Core 2 enzyme, and subsequent increased production of polylactosamine and susceptibility to galectin-1-induced apoptosis (see the Ref. 34).