Table 2.
Similarities and differences between PA and DAG in budding yeast.
| PHOSPHATIDIC ACID | DIACYLGLYCEROL | |
|---|---|---|
| Structure |
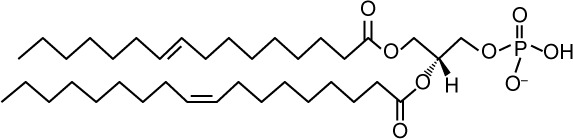
|
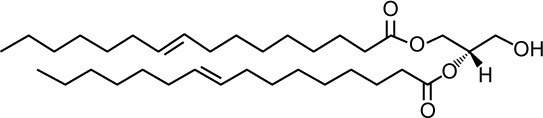
|
| Lipid shape | Cone induces negative curvature | |
| Speciesa,24,25,96 | 26:0; 26:1 28:0; 28:1 30:0; 30:1; 30:2 32:1; 32:2 34:1; 34:2 36:1; 36:2 |
|
| Headgroup charge | Negative Deprotonated: −2 Protonated: −1 |
Neutral |
| Abundanceb | 8–10 mol% (cell extract)24,96 2 mol% (TGN/E)45,97 10 mol% (PM)45 4% total PL (PM)98 0.6–2% total PL (mito)98 4% total PL (ER)98 2% total PL (vacuole)98 1.8% total PL (LD)35 |
4–6 mol% (cell extract)24,96 10 mol% (TGN/E)45,97 n.d. (PM)45 |
| Transbilayer movement26 | No | Rapid “flip flop” without protein assistance |
| Interaction with effector proteins | Electrostatic/hydrogen bond switch model65 No consensus sequence8 |
Specific, mediated by C1 consensus domain55,59 |
| Proposed roles | pH sensor68 Fusion (prospore formation)74,99 Mediates membrane recruitment of Pah1 (ER),50 Opi1 (ER),11 Spo20 (PM)73 Mitochondrial protein biogenesis100 |
Fusion (vacuole)20 Regulates protein secretion44 Membrane recruitment of Pkc1 is controversial60,61 |
Notes:
Common PA and DAG species, most abundant species are in bold.
Unless otherwise indicated, abundance is expressed as mol% of all yeast lipids, including glycerolipids, sphingolipids, and ergosterol.
Abbreviations: PL, phospholipids; TGN/E, trans-Golgi network/endosomes; PM, plasma membrane; LD, lipid droplet; mito, mitochondria; n.d., non detected.
