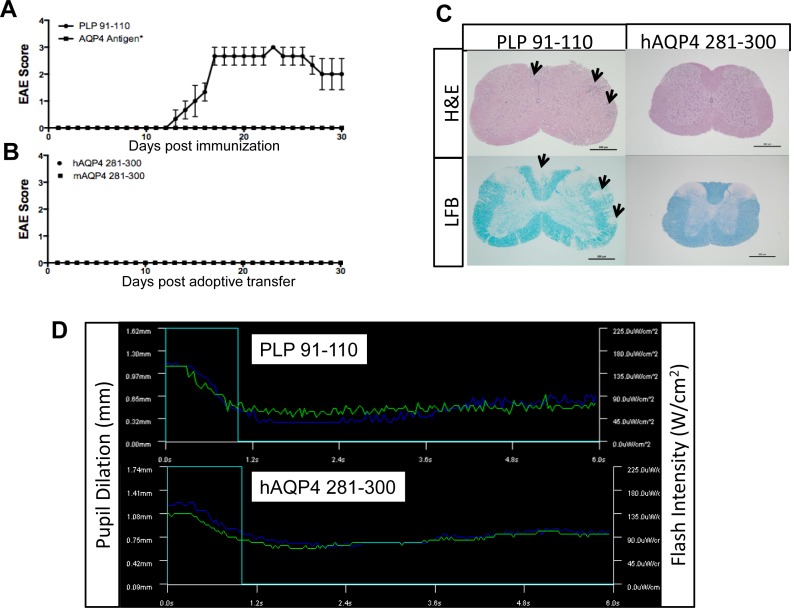
Fig 2. HLA-DRB1*03:01 transgenic mice are disease resistant to active immunization with human aquaporin 4 (hAQP4), and adoptive transfer of hAQP4-specific T cells.
(A) HLA-DRB1*03:01 mice were actively immunized with proteolipid protein (PLP)91-110 (100 μg/100 μl/mouse; positive control [25]), or varying AQP4 antigens*(whole-length hAQP4 protein, hAQP4281-300, murine (m)AQP4281-300, hAQP4281-300 with a Quil-A Incomplete Freund Adjuvant (IFA) booster on day 14 post-immunization, mAQP4281-300 with a Quil-A IFA booster on day 14 post immunization, and hAQP4281-300 plus mAQP4281-300) emulsified in Complete Freund Adjuvant (CFA). Immunization with a positive control proteolipid protein (PLP)91-110, a dominant encephalitogenic determinant in HLA-DRB1*03:01 led to typical EAE. (B) Lymph node cells taken from HLA-DRB1*03:01 mice immunized with hAQP4281-300 or mAQP4281-300 were restimulated for three days and passively transferred into HLA-DRB1*03:01 mice. None of these experimental approaches resulted in clinical disease. (C) Paraffin sections were stained with haematoxlin eosin (H&E) and luxol fast blue (LFB). Representative sections of the spinal cords from PLP91-110 and hAQP4281-300 immunized mice are shown. On histopathological examination there were no visible signs of cellular infiltration, inflammation, or demyelination within the brain and spinal cord in any experimental paradigms other than in active immunization with PLP91-110, the dominant encephalitogenic determinant in HLA-DRB1*03:01 that led to typical EAE (spinal cord shown; inflammatory infiltrates and areas of demyelination are indicated by black arrows). (D) Fifteen days post immunization of HLA-DRB1*03:01 transgenic mice with PLP91-110 or hAQP4281-300, pupillary reflex was measured via a mouse pupillometry. Mice actively immunized with hAQP4281-300 and the control antigen PLP91-110 did not show altered pupillary responses.