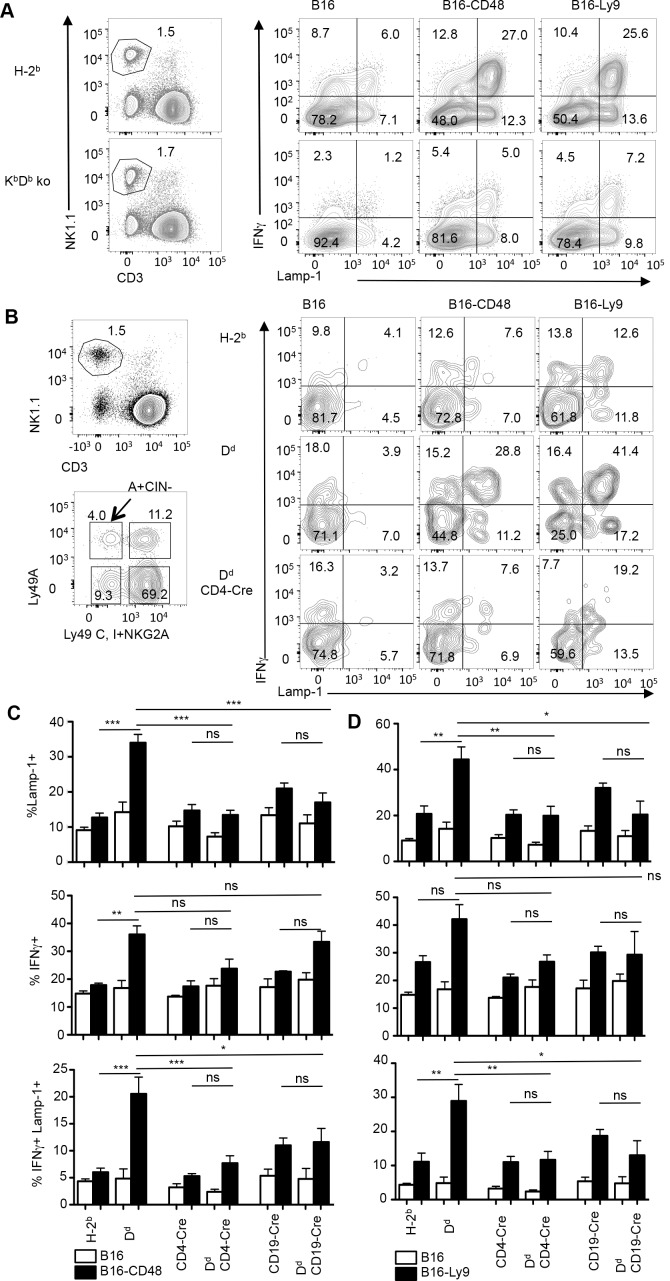
Fig 2. The activation function of CD48 and Ly9 depends on MHC class I recognition.
(A) Splenocytes from primed B6 and Kb Db knock out mice were added to B16 cells stably transfected with CD48 or Ly9 before analyzing the production of IFNγ and the release of Lamp-1 by NK cells. Data are representative of 2 determinations. (B) Splenocytes from primed H-2b mice (top row), Dd mice (middle row) Dd CD4-Cre mice (T cell-specific Dd deletion) (bottom row) were exposed to B16 cells expressing a control plasmid (B16) or B16 cells stably transfected with CD48 or Ly9 cDNA. Splenocytes were harvested and NK cells expressing Ly49A and lacking Ly49C, Ly49I and NKG2A (A+CIN-) were analyzed for their production of IFNγ and expression of cell surface of Lamp-1. (C, D) The bar graphs show mean percentage (±SEM) of IFNγ+, Lamp-1+ or IFNγ+ Lamp-1+ among A+CIN- NK cells following exposure to B16 cells (open bars) or B16 cells expressing CD48 (C) or Ly9 cDNA (D) (black bars) in 3 independent experiments using 1–2 mice in each experiment (total n = 3–6). Statistics: One-way ANOVA *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.005, ns not significant (p>0.05).