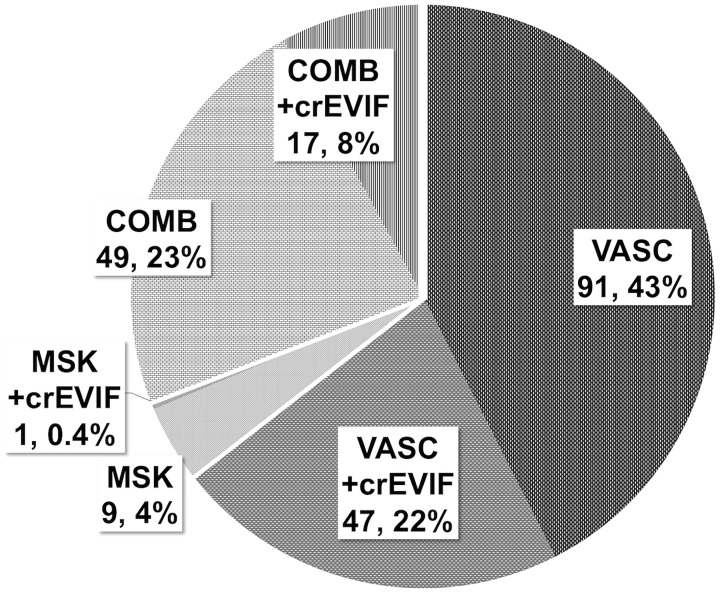
Fig 3. Pie chart for distribution of origin of intermittent claudication assessed with run-off CTA.
The chart presents the distribution and incidence of vascular (VASC), musculoskeletal (MSK), and combined (COMB) causes of intermittent claudication. Additionally, the percentage of patients with clinically relevant extravascular incidental findings (crEVIFs) is displayed for each group (+crEVIFs, shaded area). In the vast majority of cases IC is due to vascular pathology (96%). In 31% of the cases coexisting musculoskeletal findings might also explain intermittent claudication. In only 4% of cases was MSK pathology identified as the only underlying cause.