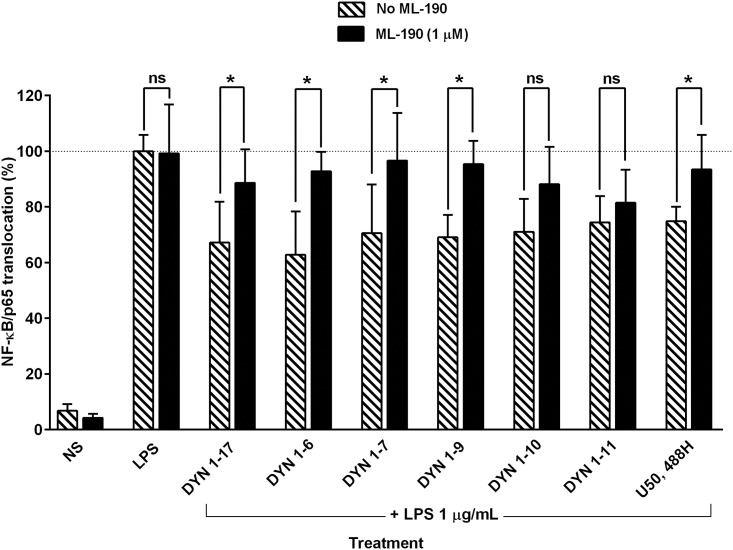
Fig 5. Effect of ML-190 on the attenuation of NF-κB/p65 nuclear translocation by DYN 1–17 and the N-terminal fragments in LPS-stimulated THP-1 cells.
The LPS-stimulated THP-1 cells were pre-treated with ML-190, a KOP receptor antagonist (1 μM, 1 hour) followed by co-treatment of the DYN 1–17 and the N-terminal fragments (10 nM) or U50,488H (10 nM) with ML-190 (1 μM, 1 hour). The treated cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde (3.7%) and immunolabelled with primary anti-NF-κB/p65 rabbit monoclonal antibody and visualized using Alexa Fluor 555® secondary antibody. DAPI staining was used to identify the nuclei. The nuclear translocation of NF-κB/p65 in each treatment group was assessed using the Image Xpress system. Non-stimulated THP-1 cells (NS) served as negative control. The percentage of NF-κB/p65 nuclear translocation in each treatment group was normalised and expressed relative to LPS-stimulated control group (contains DMSO 0.1% as diluent control). Data shown are the means ± S.E.M. of at least three independent experiments performed in triplicates, *p ≤ 0.05.