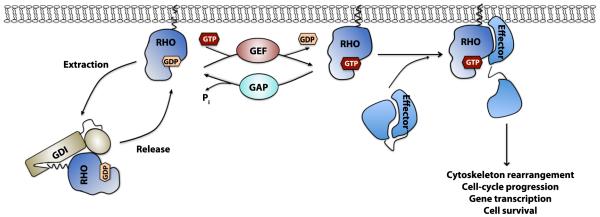
Figure 1. Biochemical model of the Rho GTPase regulatory mechanism.
Rho, Rac and Cdc42 cycle between an inactive GDP-bound and an active GTP-bound state. GEFs catalyze the GDP/GTP nucleotide exchange and activate the Rho GTPases, whereas GAPs enhance the intrinsic GTP-hydrolysis activity and inactivate them. GDIs can sequester Rho GTPases in the cytosol and prevent their activation. Activated Rho GTPases can interact with a variety of effector molecules to trigger downstream signaling events leading to diverse cellular responses.