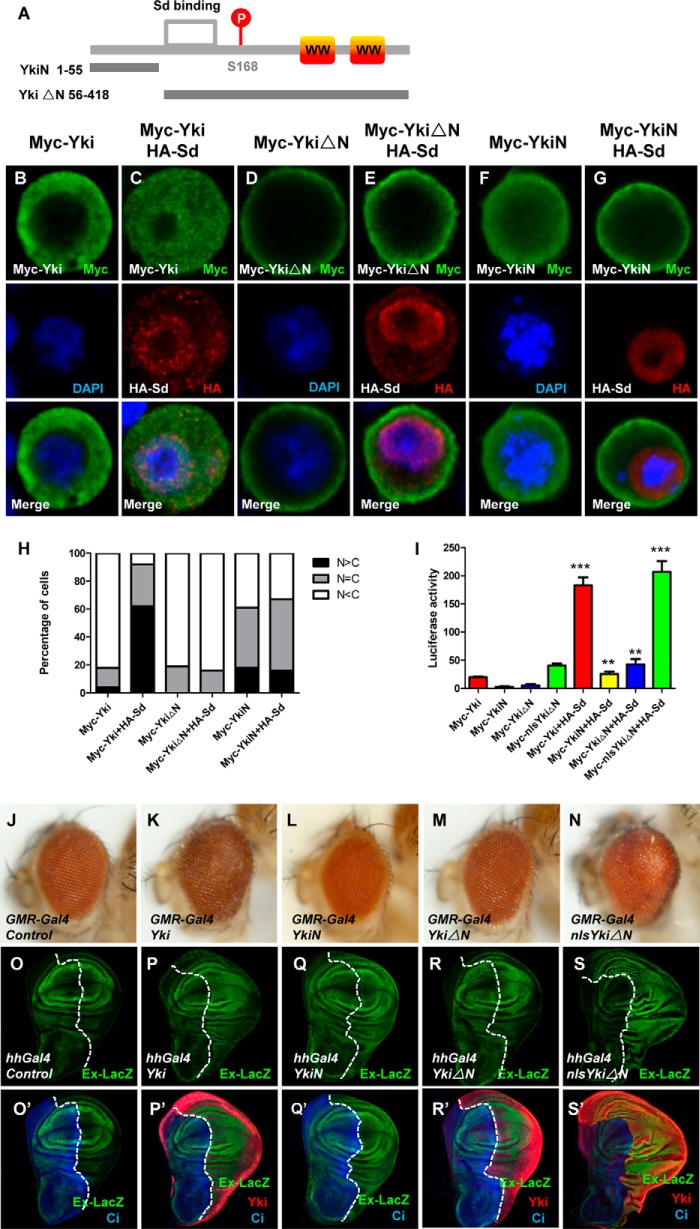
FIGURE 1.
N terminus of Yki is essential for its nuclear localization and function. A, schematic diagram of Yki and the region corresponding to YkiN/YkiΔN. Yki contains two WW domains. YkiN contains amino acids 1 to 55 and YkiΔN contains amino acids 56 to 418. B–G, S2 cells expressing Myc-Yki (B–C), Myc-YkiN (D–E), Myc-YkiΔN (F–G) with or without HA-Sd were immunostained with anti-Myc (green) or anti-HA (red) antibodies. Nuclei are marked by DAPI (blue). H, cells with different nucleocytoplasmic distributions of Myc-tagged Yki or Yki truncations were counted. A total of 100 cells were counted for each case. The y axis indicates the percentage of cells in each category. I, transcription activities of Yki, YkiN, YkiΔN, and nlsYkiΔN with or without coexpression of Sd in vitro. S2 cells were transfected with the indicated constructs and the reporter genes. 48 h post-transfection, cell lysates were harvested and subjected to a dual luciferase assay. All data are represented as the mean ± S.E. **, p < 0.01. ***, p < 0.001. J–N, side views of wild-type eyes (J) or eyes expressing Yki (K), YkiN (L), YkiΔN (M), or nlsYkiΔN (N) with GMR-Gal4. O–S′, wild-type third-instar larval wing discs (O–O′) or wing discs expressing Yki (P–P′), YkiN (Q–Q′), YkiΔN (R–R′), or nlsYkiΔN (S–S′) under the control of hhGal4 were immunostained to demonstrate the expression of Cubitus (Ci) (blue), Yki (red), Ex-lacZ (green).