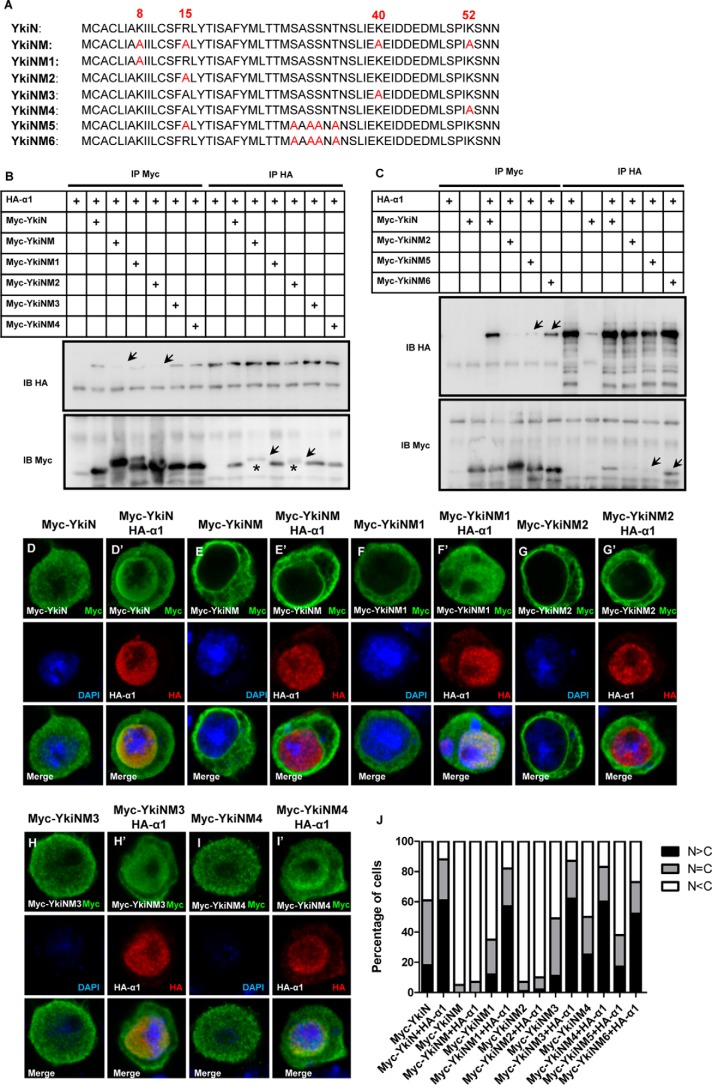
FIGURE 4.
Mapping the important sites on the Yki N terminus. A, amino acid sequence of YkiN/YkiNM/YkiNM1/YkiNM2/YkiNM3/YkiNM4/YkiNM5/YkiNM6. B, R15A point mutation of YkiN (YkiNM2) blocks its association with Importin α1. S2 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids and were immunoprecipitated, followed by Western blot analysis. C, Myc-YkiN and Myc-YkiNM6 can interact with Importin α1, while Myc-YkiNM2 or Myc-YkiNM5 cannot. S2 cells were transfected with the indicated constructs. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated and probed by anti-Myc and anti-HA antibodies. D–I′, YkiNM2 shows suppressed nuclear entrance induced by Importin α1. S2 cells were transfected with the YkiN variants and Importin α1 and then stained with anti-Myc (green) and anti-HA (red) antibodies. J, cells in D–I′ were categorized based on the anti-Myc immunostaining pattern. 100 cells were counted in each case. S2 cells expressing the indicated proteins were immunostained with the anti-Myc (green) and anti-HA (red) antibodies.