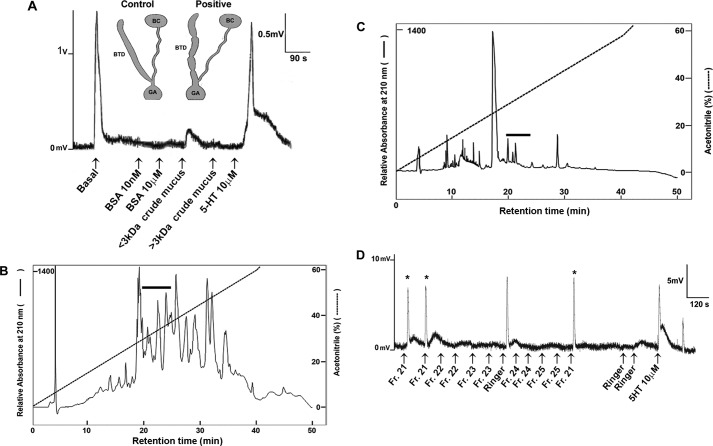
FIGURE 2.
Identification of mucous gland-associated allohormone fraction in C. aspersum. A, representative in vitro assay showing the effect of mucus extracts on contraction of the copulatory canal, which forks into two distinctive functional regions: the bursa tract diverticulum (BTD) and bursa copulatrix (BC). Delivery of each extract was issued at approximately every 90 s at a dose of 20 μl/extract. Extracts included negative controls of two levels of BSA, crude mucous gland extracts of <3 kDa and crude mucus extracts of >3 kDa, and the positive control serotonin (5-HT). Contractions (positive responses) are recorded as mV and compared with basal contractions and stimulated contractions induced by 5-HT. The schematics were adapted from Pomiankowski and Reguera (42). B, representative RP-HPLC chromatogram of a total C. aspersum mucous gland extract. The absorbance was monitored at 210 nm, and the gradient line (dotted line) shows the percentage of acetonitrile. The black bar shows the region that is bioactive in in vitro contractility assays (supplemental Table S1). C, RP-HPLC chromatogram of the C. aspersum mucous gland extract semipurified previously by a 2-ml Ultracel with a <3-kDa cutoff. The absorbance was monitored at 210 nm, and the gradient line (dotted line) shows the percentage of acetonitrile. The black bar shows the region that is bioactive in in vitro contractility assays (supplemental Table S1). D, representative in vitro assay showing the effect of RP-HPLC fractions 21–25. Delivery of each fraction was issued approximately every 120 s at a dose of 10 μl/fraction. Contractions (positive responses) are recorded as mV and compared with basal contractions and those induced by 5-HT. Asterisk indicates positive response following fraction treatment.